 [Image: Descending into Mammoth Cave, from Beneath the surface; or, the wonders of the underground world by W.H. Davenport Adams].
[Image: Descending into Mammoth Cave, from Beneath the surface; or, the wonders of the underground world by W.H. Davenport Adams].
By way of JF Ptak Science Books, I found myself reading through an old book called Beneath the surface; or, the wonders of the underground world by W.H. Davenport Adams this weekend, a travelogue from 1876 exploring subterranean landscapes around the world, including what is now Mammoth Cave National Park.
“Then we descend,” Adams writes upon his arrival at the cave, “by a small pathway excavated among the rocks, until we discover, in the sides of the mountain, and at the bottom of a funnel-shaped cavity, overgrown with verdure, an opening so low and narrow that two people can with difficulty enter at once.”
Slipping through, they pass into “a labyrinth of caves” consisting of seemingly endless sloping rooms, shafts, and corridors.
As my own phrasing there indicates, these spaces are described by way of architectural analogy: as naves and vestibules, chambers and rotundas. In fact, their perceived architectural characteristics are highlighted even on the acoustic level. One cave, for example, is a place “where the voice resounds and, lingering, reverberates, like the strain of an organ through dim cathedral aisles.”
 [Image: A room in Mammoth Cave known as “The Maelstrom,” from Beneath the surface; or, the wonders of the underground world by W.H. Davenport Adams].
[Image: A room in Mammoth Cave known as “The Maelstrom,” from Beneath the surface; or, the wonders of the underground world by W.H. Davenport Adams].
Continuing on their downward trek, Adams & Co. soon wander into “a chamber nearly 320 feet in circuit, whose roof rises like the stand of an immense nave. Its form, its grandeur, its magnitude (it could accommodate five thousand persons), and the strange architectural-like stalactites which embellish it, have procured it the name of the Gothic Church.”
Indeed, standing amidst this ersatz cathedral, and “thanks to the power of imagination, and the varying influence of the light, we here distinguish all the details of a medieval nave, pillars, and columns, and corbels and ogives.”
Among many things, what interests me here is how the interior of the earth is seen as if through the haze of a projection, with architectural forms emerging where, in fact, only inhuman geological processes at work—but also, in the opposite direction, the implied observation here that, in an age of masonry construction, architecture and geology were, in effect, natural cousins, lending themselves to mutual comparison far more easily than in today’s time of glass and steel construction.
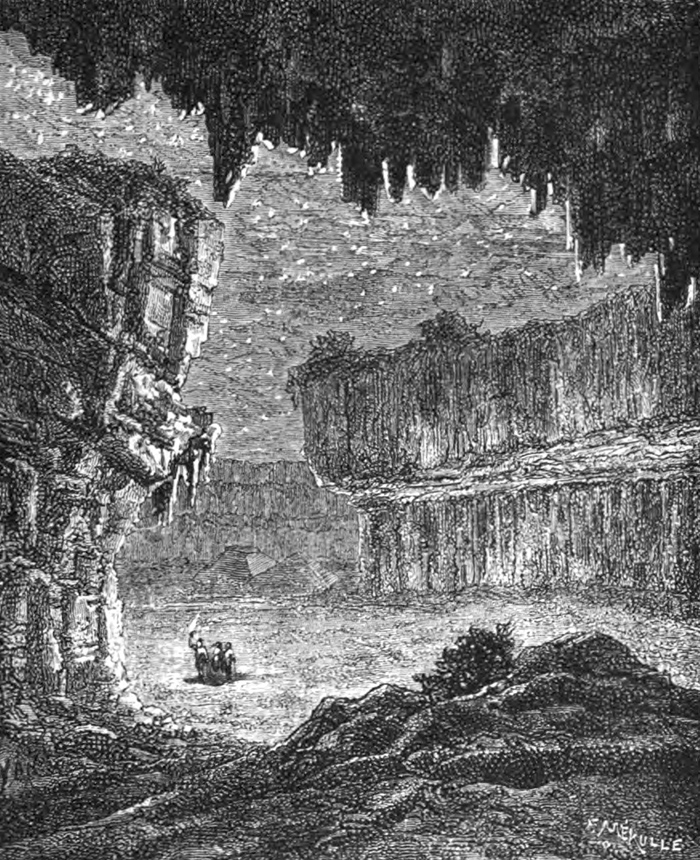 [Image: A vast underground room filled with “a silent, terrible solitude,” from Beneath the surface; or, the wonders of the underground world by W.H. Davenport Adams].
[Image: A vast underground room filled with “a silent, terrible solitude,” from Beneath the surface; or, the wonders of the underground world by W.H. Davenport Adams].
To put this another way, many streets in Manhattan are often quite appropriately described as “canyons,” not only due to their perceived depth—that is, given the towering buildings on either side, as if pedestrians merely wander at the bottom of artificial slot canyons—but also due to the geological materials those buildings were made from.
However, following widespread transformations in global building construction, our buildings today are now more likely to be reflective—even dangerously so—or partially transparent, whether this is due to the use of glass curtain walls or shadow-annihilating polished titanium, with the effect that our urban environment is no longer particularly well-served by geological analogy.
In any case, the book’s flirtation with an architectural vocabulary is gradually abandoned as Adams and his colleagues venture deeper into the planet. They eventually find themselves standing somewhat uncomfortably surrounded by a “phantasmagoria” of black gypsum walls, all “covered with sparkling crystallizations,” in a vast room whose belittling proportions inspire feelings not of grandeur and religiosity but a kind of exhausted desolation.
Here, Adams writes, “you think yourself on one of those dead and naked planets, where mineral nature reigns in the bosom of a silent, terrible solitude; on some earth never warmed by the sun, and which is animated by no kind of life.”
 [Image: An unfortunately rather low-res image from Beneath the surface; or, the wonders of the underground world by W.H. Davenport Adams].
[Image: An unfortunately rather low-res image from Beneath the surface; or, the wonders of the underground world by W.H. Davenport Adams].
The rest of the book—including the image seen immediately above this sentence—ventures elsewhere, into silver mines and glacial caves, even briefly passing by way of underground “artificial ice caves” for the premodern production and storage of ice.
I’m just a sucker for subterranea. Check it out if any of this sounds up your alley, and click through the archives of JF Ptak Science Books while you’re at it.
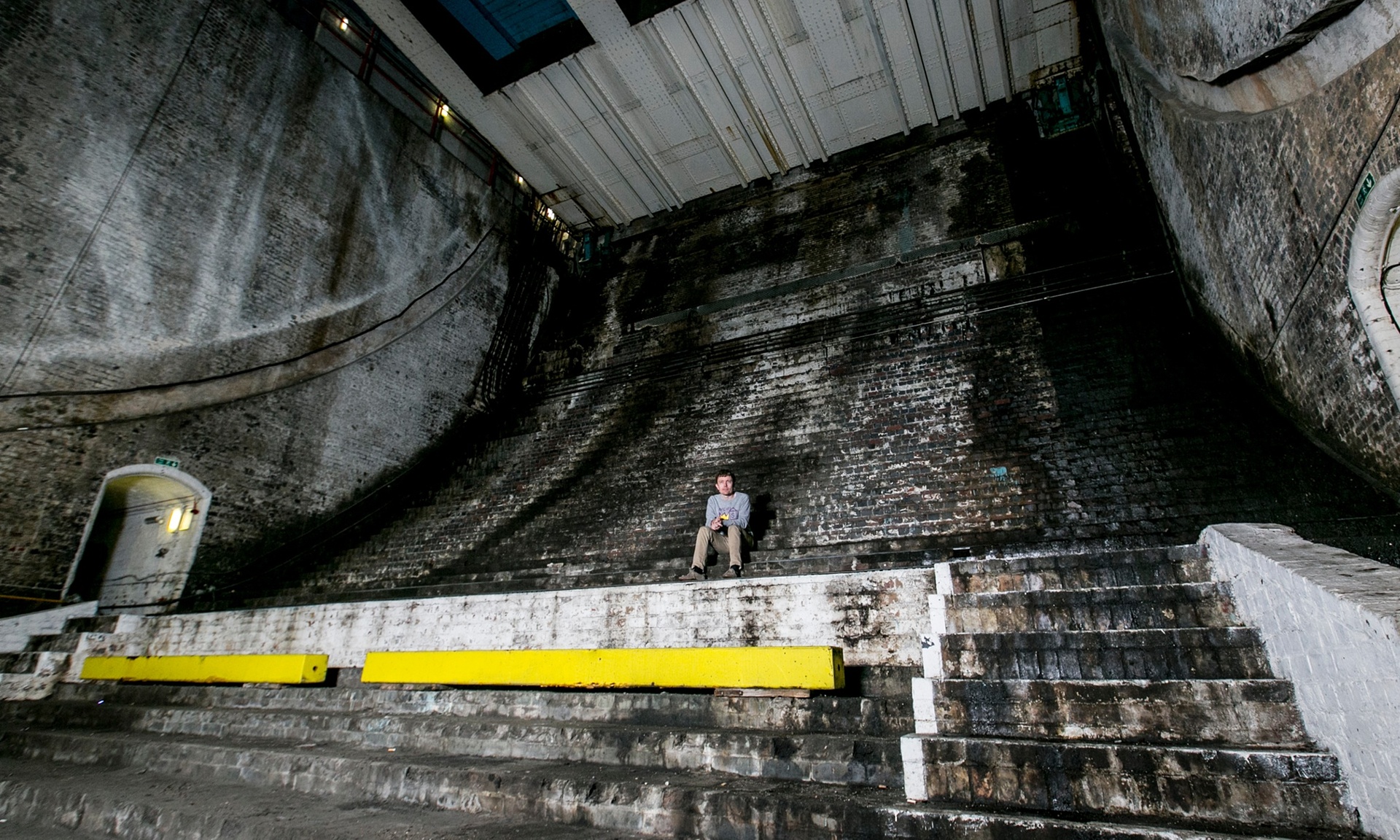

 [Image: Photo by
[Image: Photo by 
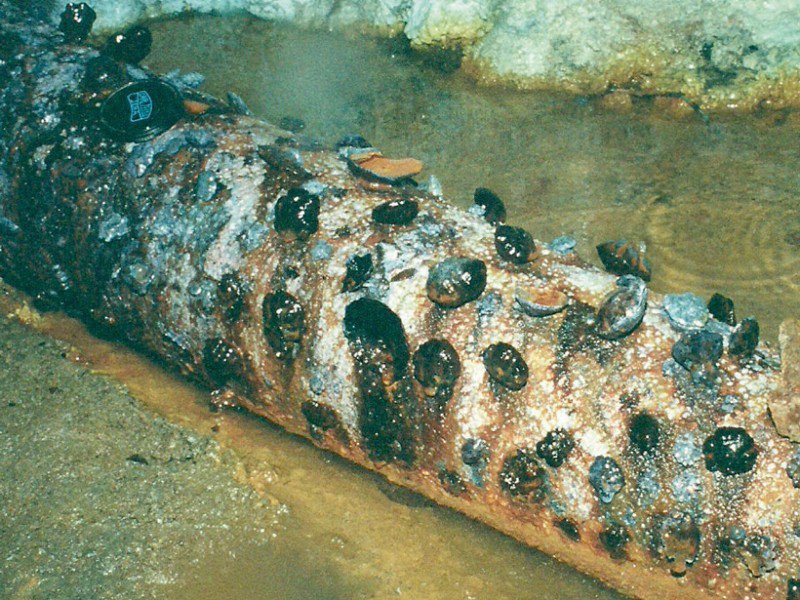 [Image: Metal shells growing in the darkness of abandoned mines; photo by
[Image: Metal shells growing in the darkness of abandoned mines; photo by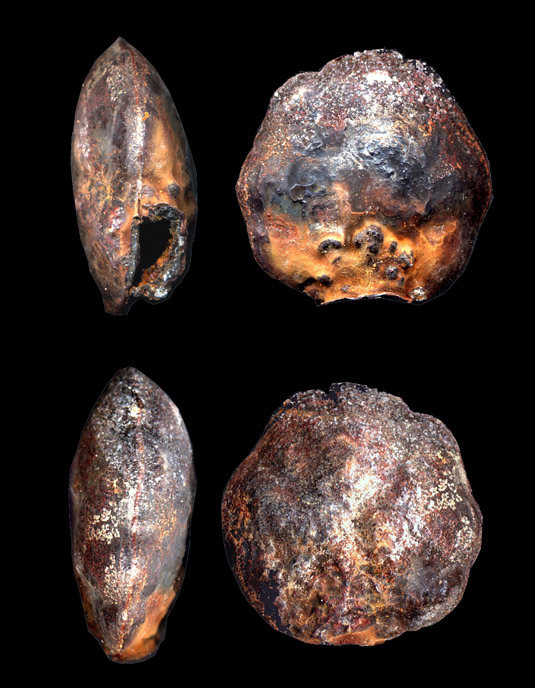  [Image: Metal shells growing in the darkness of abandoned mines; photo by
[Image: Metal shells growing in the darkness of abandoned mines; photo by  [Image: An “
[Image: An “
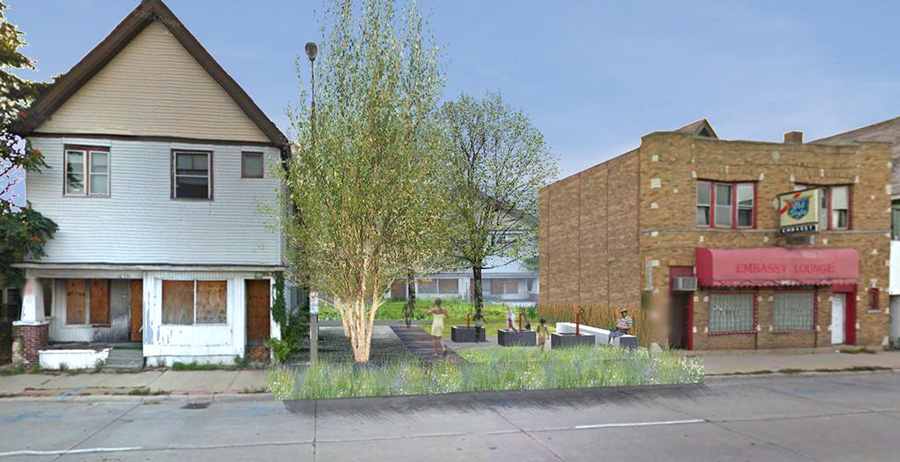 [Image: Rendering of a possible “BaseTern” landscape by students Brett Harris, Andrew D’Arcy, and Heidi Petersen, via
[Image: Rendering of a possible “BaseTern” landscape by students Brett Harris, Andrew D’Arcy, and Heidi Petersen, via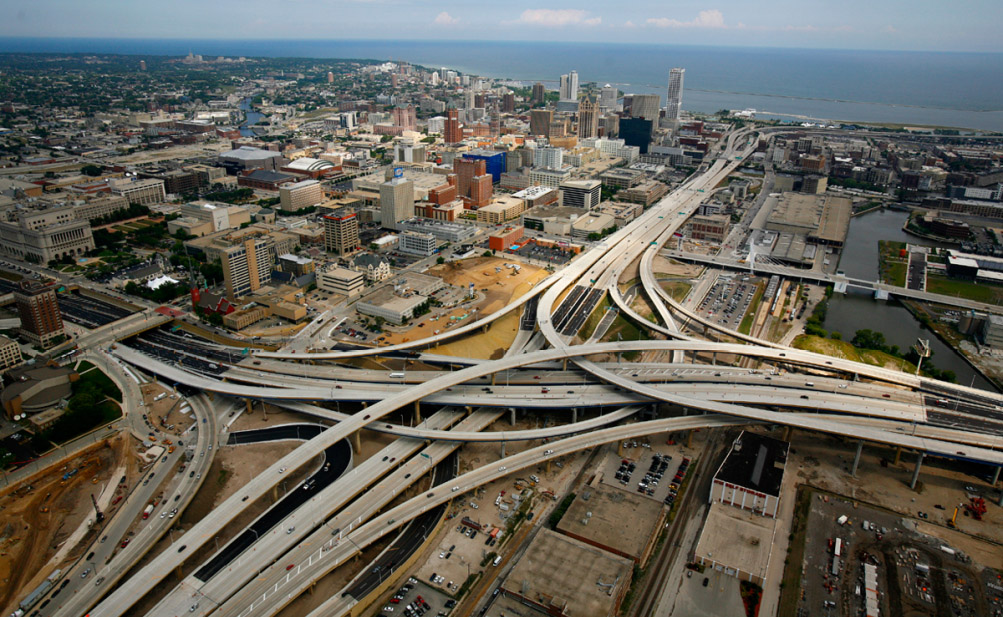 
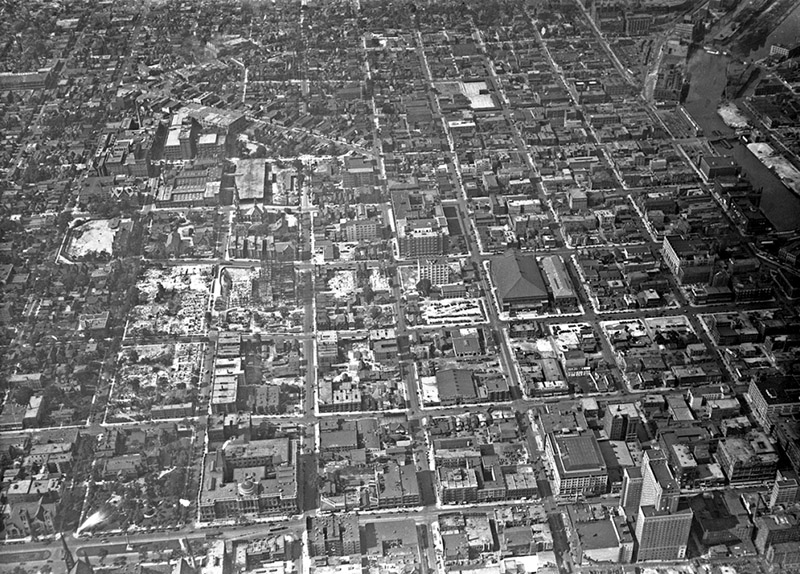 [Images: (top) Milwaukee’s Marquette interchange, nearly the same size as the city it cuts through; (bottom) Milwaukee before the interchange. Images via
[Images: (top) Milwaukee’s Marquette interchange, nearly the same size as the city it cuts through; (bottom) Milwaukee before the interchange. Images via 
 [Images: Two BaseTern design diagrams, taken from Milwaukee’s “
[Images: Two BaseTern design diagrams, taken from Milwaukee’s “
 [Image: “Riggers install a lightning rod” atop the Empire State Building “in preparation for an investigation into lightning by scientists of the General Electric Company” (1947), via the
[Image: “Riggers install a lightning rod” atop the Empire State Building “in preparation for an investigation into lightning by scientists of the General Electric Company” (1947), via the  [Image: Lightning storm over Boston; via
[Image: Lightning storm over Boston; via  [Image: Lightning via
[Image: Lightning via 
 [Image: Photo by & courtesy of
[Image: Photo by & courtesy of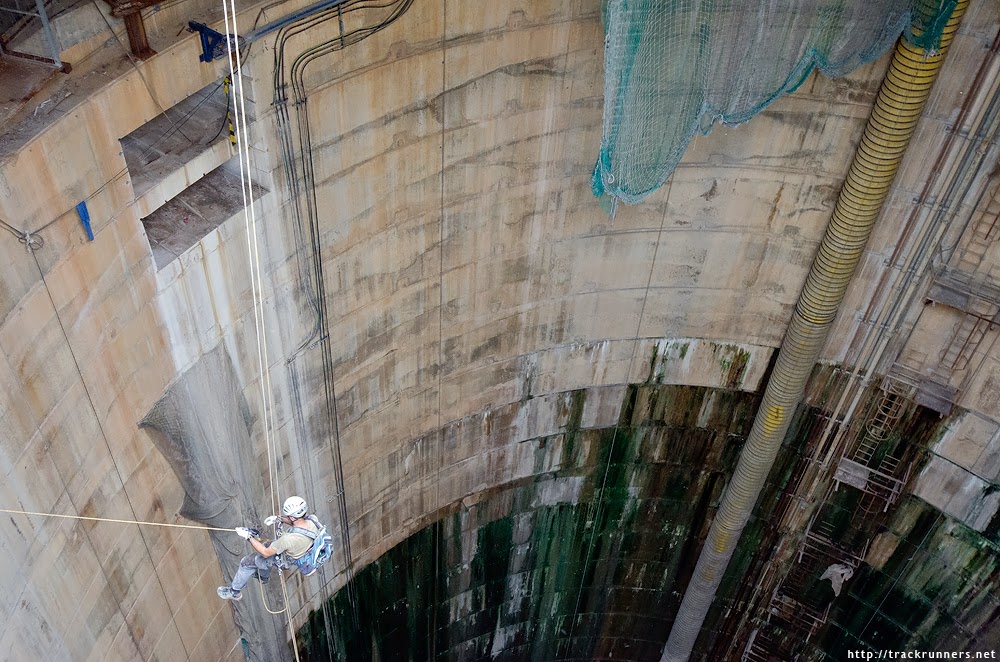 
 [Images: Photos by & courtesy of
[Images: Photos by & courtesy of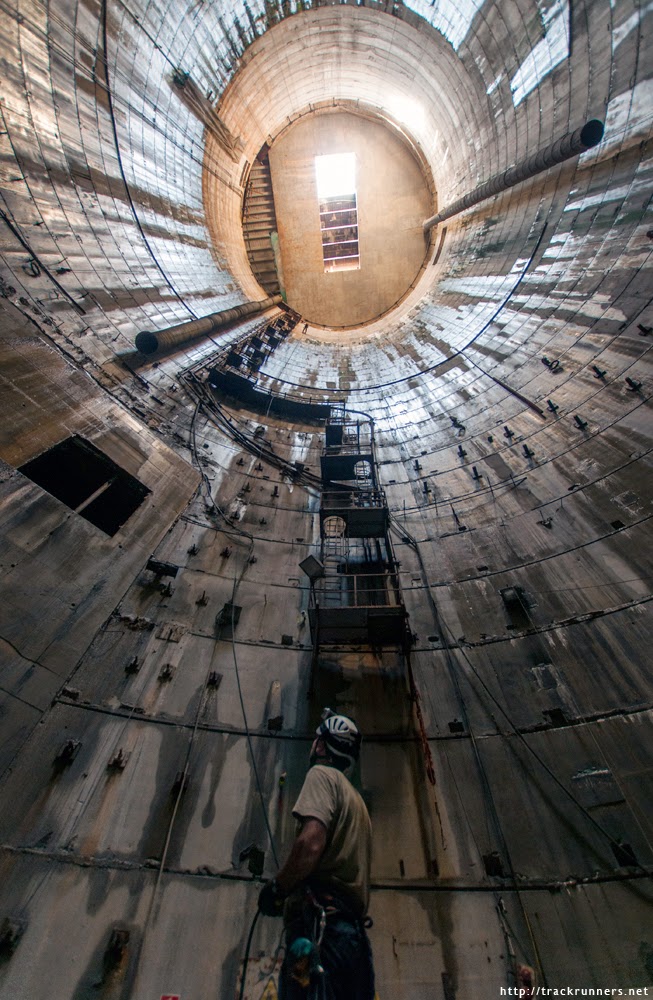  [Image: Photo by & courtesy of
[Image: Photo by & courtesy of  [Image: Photo by & courtesy of
[Image: Photo by & courtesy of  [Image: Photo by & courtesy of
[Image: Photo by & courtesy of  [Image: Photo by & courtesy of
[Image: Photo by & courtesy of  [Image: Photo by & courtesy of
[Image: Photo by & courtesy of 
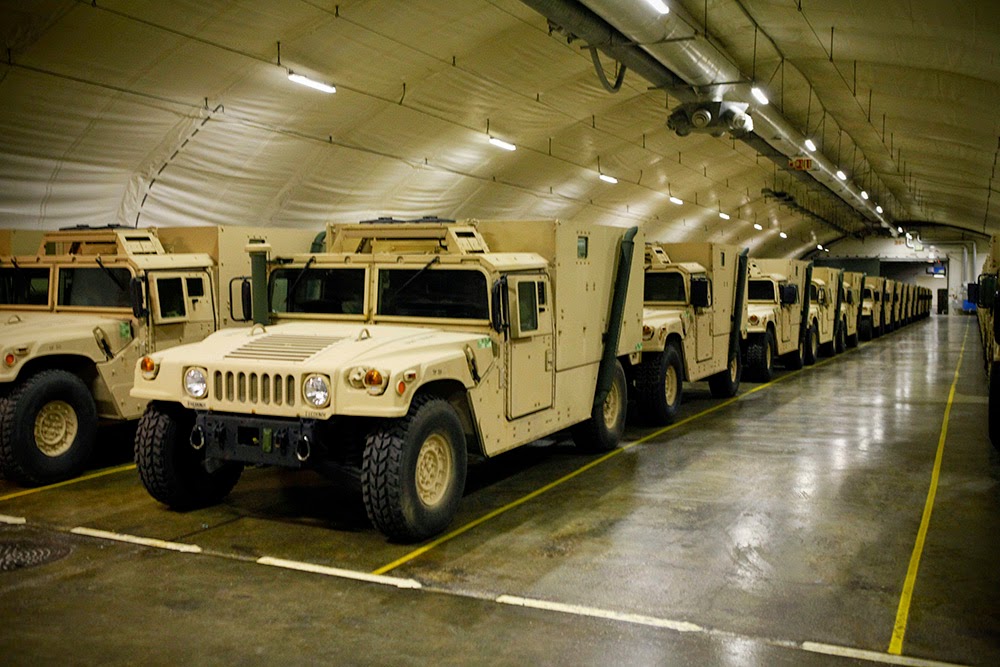 [Image: “Humvees are stored inside the Frigaard Cave in central Norway. The cave is one of six caves that are part of the Marine Corps Prepositioning Program-Norway, which supports the equipping of Marine Expeditionary Brigade consisting of 15,000 Marines and with supplies for up to 30 days.”
[Image: “Humvees are stored inside the Frigaard Cave in central Norway. The cave is one of six caves that are part of the Marine Corps Prepositioning Program-Norway, which supports the equipping of Marine Expeditionary Brigade consisting of 15,000 Marines and with supplies for up to 30 days.”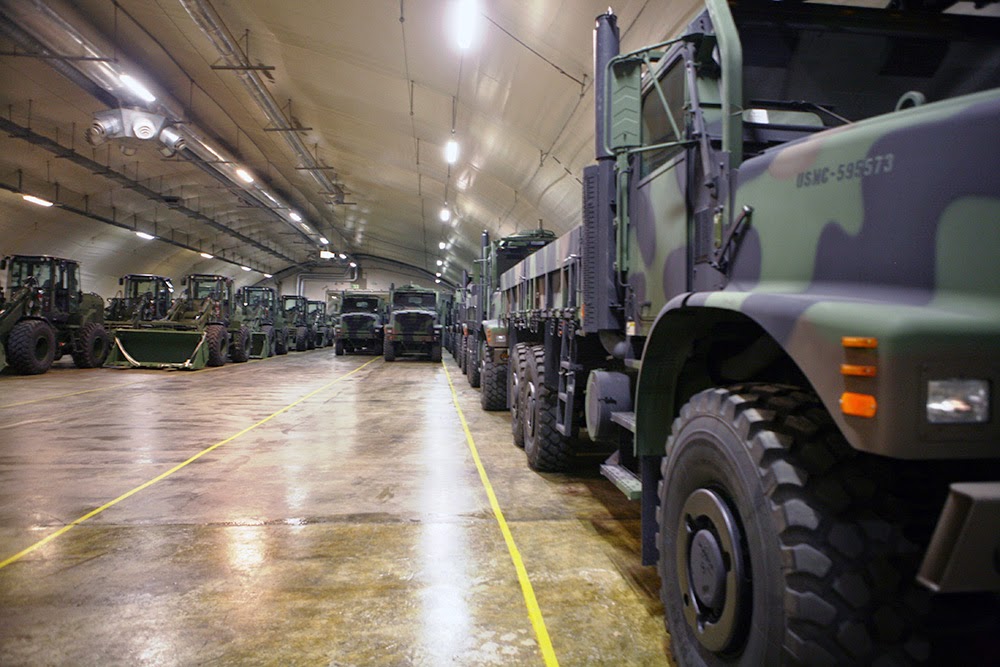  [Image: “Rows of front loaders and 7-ton trucks sit, gassed up and ready to roll in one of the many corridors in the Frigard supply cave located on the Vaernes Garrison near Trondheim, Norway. This is one of seven [see previous caption!] caves that make up the Marine Corps Prepositioning Program-Norway facility. All the caves total more than 900,000 sq. ft. of storage space, full of enough gear to outfit 13,000 Marines for up to 30 days.”
[Image: “Rows of front loaders and 7-ton trucks sit, gassed up and ready to roll in one of the many corridors in the Frigard supply cave located on the Vaernes Garrison near Trondheim, Norway. This is one of seven [see previous caption!] caves that make up the Marine Corps Prepositioning Program-Norway facility. All the caves total more than 900,000 sq. ft. of storage space, full of enough gear to outfit 13,000 Marines for up to 30 days.”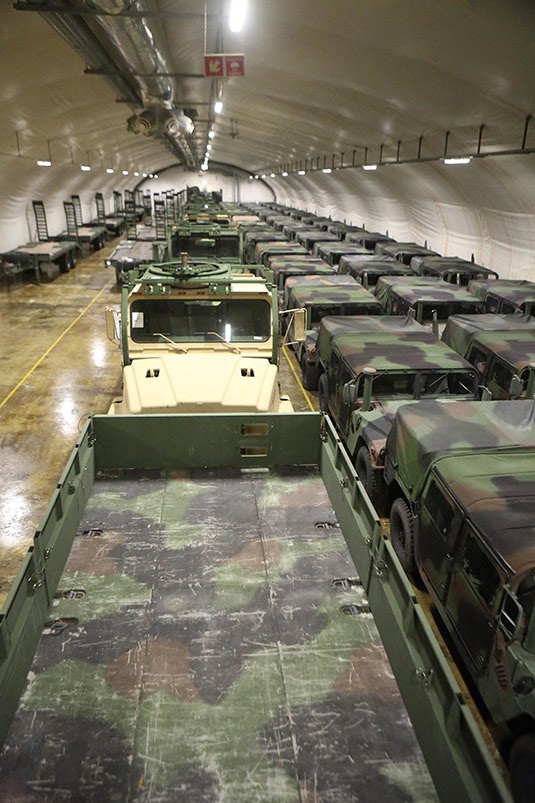  [Image: “Medium Tactical Vehicle Replacements, High Mobility Multipurpose Wheeled Vehicles and trailers, which belong to Marine Corps Prepositioning Program-Norway are staged in a storage cave at Tromsdal, Norway, Feb. 24, 2014. Marine Corps began storing equipment in several cave sites throughout Norway in the 1980s to counter the Soviets, but the gear is now reserved for any time of crisis or war.”
[Image: “Medium Tactical Vehicle Replacements, High Mobility Multipurpose Wheeled Vehicles and trailers, which belong to Marine Corps Prepositioning Program-Norway are staged in a storage cave at Tromsdal, Norway, Feb. 24, 2014. Marine Corps began storing equipment in several cave sites throughout Norway in the 1980s to counter the Soviets, but the gear is now reserved for any time of crisis or war.”  [Image: “China: ample space for a spare copy of France”; image by
[Image: “China: ample space for a spare copy of France”; image by 
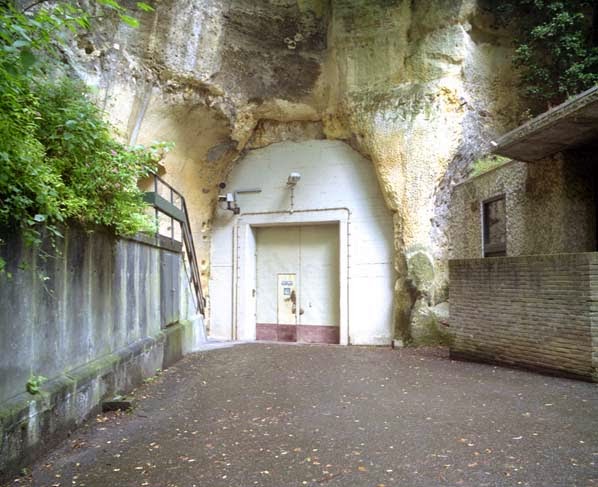 [Image: An entrance to the quarry in Kanne; photo by
[Image: An entrance to the quarry in Kanne; photo by  [Images: Monks underground; via
[Images: Monks underground; via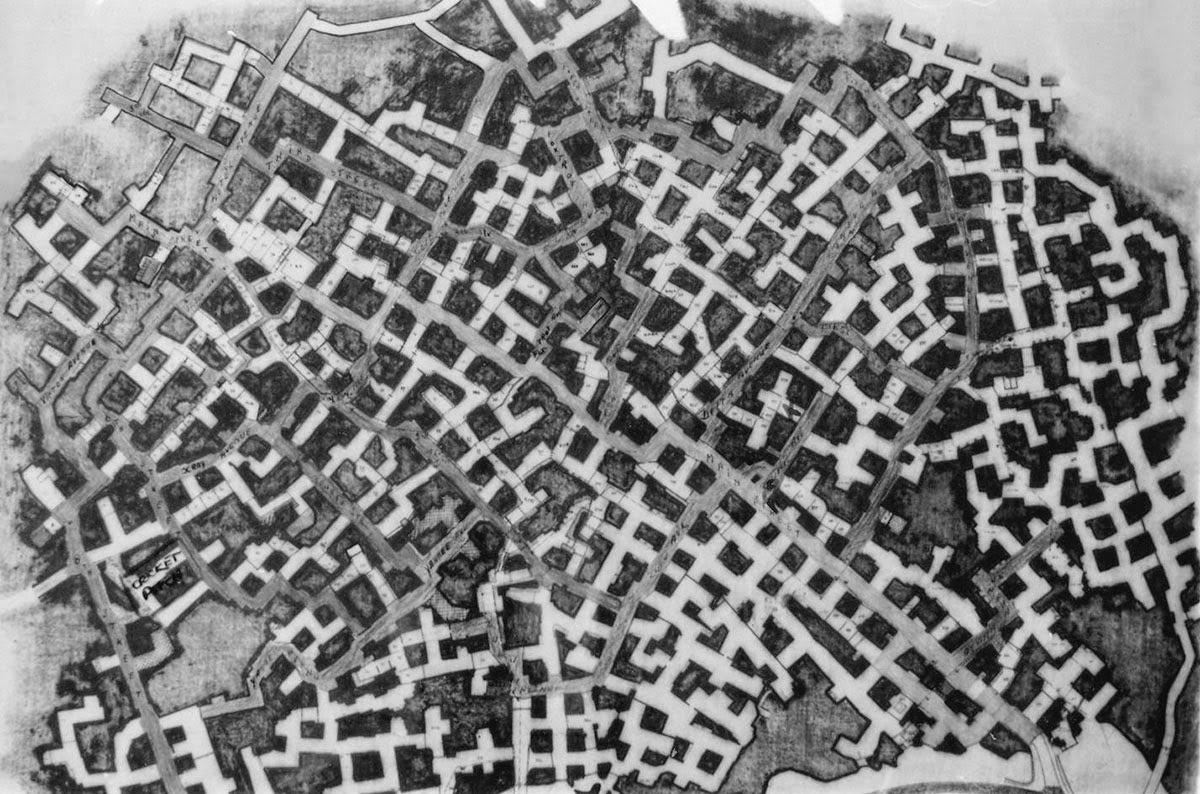  The “streets” were named, but not always easy to follow; however, this didn’t stop officers stationed there from occasionally going out to explore the older tunnels at night. A former employee named Bob Hankinson describes how he used to navigate:
The “streets” were named, but not always easy to follow; however, this didn’t stop officers stationed there from occasionally going out to explore the older tunnels at night. A former employee named Bob Hankinson describes how he used to navigate: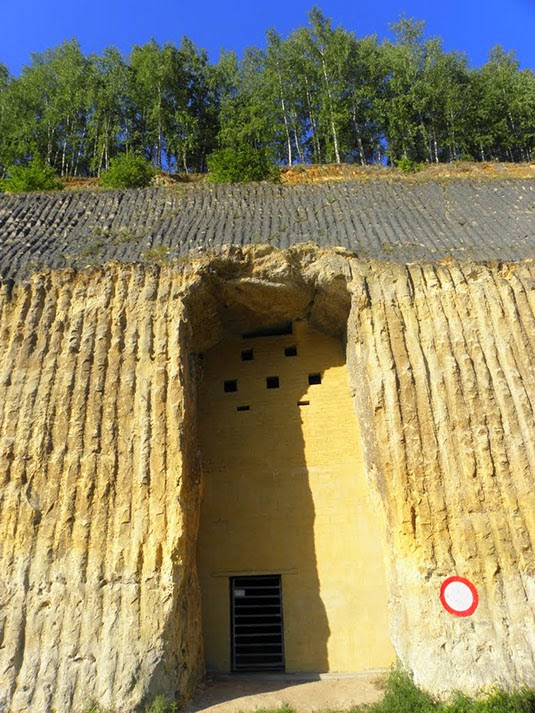  [Image: An entrance into the NATO complex;
[Image: An entrance into the NATO complex; 
 [Image: The “
[Image: The “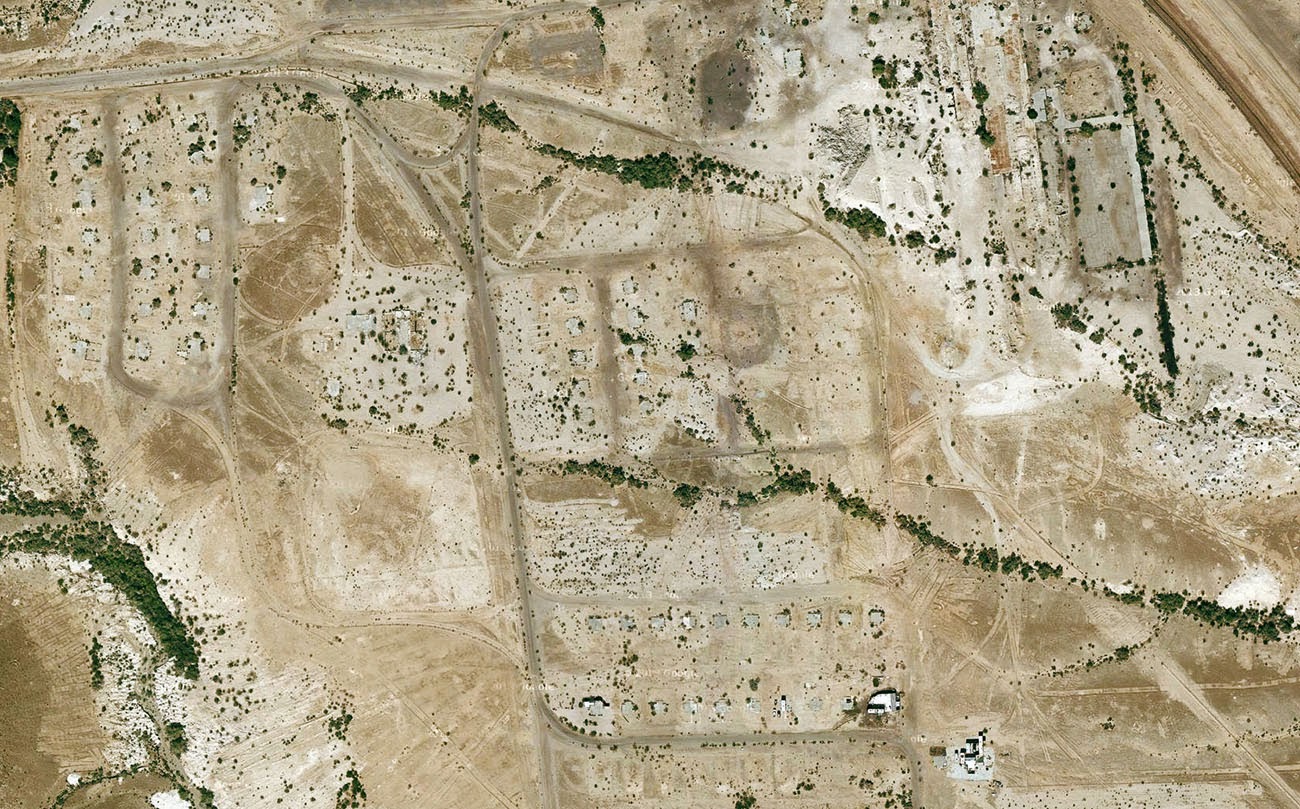 [Image: Midland, California, via
[Image: Midland, California, via  [Image: Midland, California, via
[Image: Midland, California, via  [Image: The abandoned streets of
[Image: The abandoned streets of  [Image: Midland, California, via
[Image: Midland, California, via 
 [Image: Courtesy of
[Image: Courtesy of  [Image: Courtesy of
[Image: Courtesy of  [Image: Courtesy of
[Image: Courtesy of  [Image: A Metropolitan Transportation Authority worker steps forward into the
[Image: A Metropolitan Transportation Authority worker steps forward into the