 [Image: Quarantine facility and hospital ward on Swinburne Island, in the NYC archipelago].
[Image: Quarantine facility and hospital ward on Swinburne Island, in the NYC archipelago].
It’s been an extremely eventful month since Edible Geography and BLDGBLOG teamed up to announce “Landscapes of Quarantine,” an eight-week, intensive, independent design studio to be hosted this fall in New York City; its brief is to create original and thought-provoking design projects that explore the spatial implications of quarantine. The results of the studio will then be the subject of an exhibition at Storefront for Art and Architecture in spring 2010.
The practice of quarantine extends far beyond questions of epidemic control and pest containment strategies to touch on urban planning, geopolitics, international trade, ethics, immigration, and more. In the early twentieth century, for example, “quarantine lines in Africa offered a clear and politically useful demarcation for new ‘international’ borders between Sudan and Egypt,” as historian Alison Bashford points out in her book Medicine at the Border.
From Boccaccio’s Decameron and disinfected mail protocols to bio-secure airlocks, plant smuggling, and Matt Leacock’s Pandemic boardgame, quarantine is a fertile territory for architects and designers to explore.
You can read more about the studio here.
Over the past few weeks, we have been blown away by the quality (and even quantity) of applicants interested in the studio. Indeed, narrowing the pool down to a manageable group of participants has been a very tricky process. We have been concerned all along with achieving a usefully diverse mix of backgrounds, media, and individual strategies of approach, while holding numbers low enough that the studio can still function as a weekly discussion group.
 [Image: U.S. “Federal and State Isolation and Quarantine Authority,” updated January 18, 2005].
[Image: U.S. “Federal and State Isolation and Quarantine Authority,” updated January 18, 2005].
We are now excited to announce a truly amazing list of participants:
—Joe Alterio — Illustrator, Animator, and Comic Book Artist (http://joealterio.com/)
Joe Alterio is an illustrator, animator, comic creator, and artist, interested in narrative structure, collective creativity, and the physical manifestations of story-telling. Joe has been at the forefront on using new technology to push forward the graphic narrative medium, from his early 2004 mobile comic The Basic Virus to his most recent work with Robots and Monsters. Alterio’s work has appeared in the Boston Globe, Rolling Stone, Boing Boing, Drawn!, The BLDGBLOG Book, and many other publications.
 [Image: Joe Alterio, from Robots and Monsters].
[Image: Joe Alterio, from Robots and Monsters].
—Elizabeth Ellsworth and Jamie Kruse – Artists, smudge studio (http://smudgestudio.org/)
Elizabeth Ellsworth and Jamie Kruse are co-directors of smudge studio, a collaborative, non-profit media arts studio based in Brooklyn. Ellsworth is Associate Provost of Curriculum and Learning and Professor of Media Studies at The New School. Her recent book, Places of Learning: Media, Architecture, Pedagogy is about the aesthetics of mediated learning environments. Kruse is an artist, independent scholar, and freelance graphic designer.
—Scott Geiger — Writer, Architecture Research Office (http://www.aro.net/)
Scott Geiger is the recipient of a Pushcart Prize for fiction. A contributor to magazines such as The Believer and Conjunctions, Geiger also writes for Architecture Research Office, a 2009 Finalist for the National Design Award for Architecture. As a Cleveland native, schemes to rescue America’s postindustrial cities stalk his work.
—Yen Ha and Michi Yanagishita — Architects, Front Studio (http://www.frontstudio.com/) and “ladies who lunch” (http://lunchstudio.blogspot.com/)
Yen Ha and Michi Yanagishita are principals of Front Studio Architects, named one of the “world’s 50 hottest young architectural practices” by Wallpaper magazine. Their work has been featured internationally in Icon, AD: Cities of Dispersal, and the New York Times, and it was recently featured in the London Yields exhibition at the Building Centre in London. The Invisible Gate, their competition entry in the 2005 Gdansk International Outdoor Art Gallery, is currently under construction.

 [Image: Front Studio, Farmadelphia].
[Image: Front Studio, Farmadelphia].
—Katie Holten — Artist (http://www.katieholten.com/)
Katie Holten has exhibited widely in Europe and the United States, and, in 2003, she represented Ireland at the Venice Biennale. She currently has a solo exhibition at The Bronx Museum of the Arts and a public artwork installed in the Bronx, called the Tree Museum. Holten was born in Dublin, Ireland, and is now based in New York City.
—Jeffrey Inaba — Architect, INABA Projects (http://www.inabaprojects.com/), Director, C-LAB (http://c-lab.columbia.edu/), and Editor, Volume Magazine (http://volumeproject.org/)
Jeffrey Inaba is the Director of C-Lab, an architecture, policy and communications think tank at Columbia University‘s GSAPP, and he is Features Editor of Volume Magazine. With Rem Koolhaas, Inaba co-directed the Harvard Project on the City, a research program investigating contemporary urbanism and planning worldwide. Before starting INABA, he was a principal of AMO, the research consultancy founded by Koolhaas. Inaba has also taught at UCLA, Harvard, and SCI-Arc, and he lectures worldwide.
—Ed Keller — Architect and Filmmaker, AUM Studio (http://www.aumstudio.org/)
Ed Keller is a designer, professor, writer, “media architect,” and former professional rock climber. He is co-founder with Carla Leitao of AUM Studio, an architecture and new media firm based in New York and Lisbon. Keller is an Associate Professor at Parsons School of Design, and he has taught at Columbia’s GSAPP, SCI-Arc, Pratt, the University of Pennsylvania, and more. Keller’s work has been featured in ANY, AD, Wired, Metropolis, Assemblage, among others.
—Mimi Lien — Set Designer (http://www.mimilien.com/)
Mimi Lien is a designer of sets and environments for theater, dance, and opera. After studying architecture at Yale University, she began making paintings, installations, objects, and designs for performance. Her work has been seen at The Joyce and The Kitchen, and she is a recipient of a 2007-2009 NEA/TCG Career Development Program award.
 [Image: Mimi Lien, from a set design for Samuel Beckett’s Endgame].
[Image: Mimi Lien, from a set design for Samuel Beckett’s Endgame].
—Richard Mosse — Photographer (http://www.richardmosse.com/)
Richard Mosse is an Irish photographer based in New York. He travels extensively with the assistance of a Leonore Annenberg Fellowship in the Performing and Visual Arts. Recent forays have taken him to Gaza, the Yukon Territories, and Iraq. Mosse has a forthcoming solo show at Jack Shainman Gallery, opening on November 19th, and new video work will be exhibited at Barcelona’s Ca L’Arenas, in a year-long exhibition cycle, investigating war and its representations.
 [Image: Richard Mosse, ruined swimming pool at the palace of Uday Hussein, Jebel Makhoul, Iraq].
[Image: Richard Mosse, ruined swimming pool at the palace of Uday Hussein, Jebel Makhoul, Iraq].
—Daniel Perlin — Sound Designer, Perlin Studios (http://danielperlin.net/)
Daniel Perlin is a New York-based artist and sound designer. Perlin operates across media, creating video, objects, installations and performances. His work has been heard at Chelsea Art Museum, the Whitney Biennial 2006, D’Amelio Terras, TN Probe Tokyo, Temporary Contemporary Gallery, the Centre Pompidou, and BCA (Beijing), as well as in such films as Kelly Reichardt’s Old Joy, Errol Morris’s Fog Of War and Phil Morrison’s Junebug.
—Thomas Pollman — Architect, NYC Office of Emergency Management (http://www.nyc.gov/oem and http://www.thomaspollman.com/)
Thomas Pollman is an architect and amateur cartographer based in New York City. He currently works in the Geographic Information Systems Division at the NYC Office of Emergency Management, where he works to enhance situational awareness for first responders through the deployment of geospatial technologies. Pollman is a registered architect in the State of New York.
—Kevin Slavin — Urban Games Designer, Area/Code (http://areacodeinc.com/)
Kevin Slavin is managing director and co-founder of Area/Code. Working with media companies, museums, brands, and foundations around the world, Area/Code focuses on games with computers in them. Their work frequently extends game systems into the real world—and the other way around. Prior to founding Area/Code, Slavin was an artist and an advertising executive.
—Brian Slocum — Architect, Polshek Partnership Architects (http://www.polshek.com/)
Brian Slocum is the recipient of a 2008 grant from the New York State Council on the Arts for ad hoc infrastructures, a design research project focusing on the deployment of scaffolding and alternatives for its spatial exploitation. Slocum was a contributor to Pamphlet Architecture #23 and is currently an Associate at Polshek Partnership Architects.
—Amanda Spielman — Graphic Designer, Graphomanic (http://www.graphomanic.net/) and SpotCo (http://www.spotnyc.com/)
Amanda Spielman is a graphic designer at SpotCo, a New York-based design studio and ad agency that specializes in creating artwork for Broadway theater. Previously, she spent seven years in editorial design. Her work has appeared in The Design Entrepreneur, Fingerprint, Graphis, STEP, SPD, and metropolismag.com. Spielman graduated from the MFA Design program at the School of Visual Arts, and holds a BA from Vassar College.
 [Image: Amanda Spielman, Island of New Ephemera].
[Image: Amanda Spielman, Island of New Ephemera].
—Lebbeus Woods — Architect, Author, and Educator (http://lebbeuswoods.wordpress.com/ and http://lebbeuswoods.net/)
Lebbeus Woods is an architect and educator. He is co-founder of RIEA.ch, an institute devoted to the advancement of experimental architectural thought and practice, and author of Pamphlet Architecture #6 and #15, among countless other articles and books. His works are held in private and public collections worldwide, including the Museum of Modern Art and the Austrian Museum of Applied Arts, Vienna. Woods has received the Progressive Architecture Award for Design Research, the American Institute of Architects Award for Design, and the Chrysler Award for Innovation in Design. He is currently Professor of Architecture at The Cooper Union in New York City.
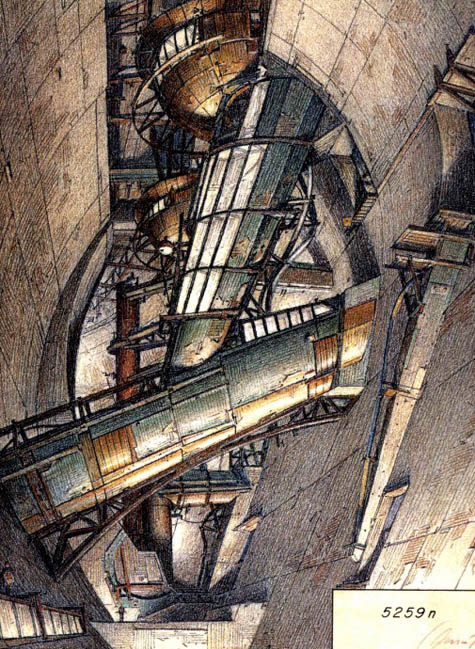 [Image: Lebbeus Woods, from a film treatment for Underground Berlin].
[Image: Lebbeus Woods, from a film treatment for Underground Berlin].
It’s hard to overstate how honored we are to work with practitioners of this caliber; we look forward to eight solid weeks of inspiring conversations and even more interesting work.
Expect frequent updates throughout the fall – in particular, during the week of October 5th, when we will begin to publish, both on Edible Geography and on BLDGBLOG, a series of original interviews with quarantine historians, public health policy experts, biosafety consultants, and more, placing quarantine into its unpredictably extensive context.
By making the studio discussions and our own research material public, we hope that anyone who has been inspired by the studio brief – and by the subject matter of quarantine – will be inspired to pursue their own projects, outside the necessarily limited walls of the studio.
 [Image: The
[Image: The  [Image: Brains].
[Image: Brains].
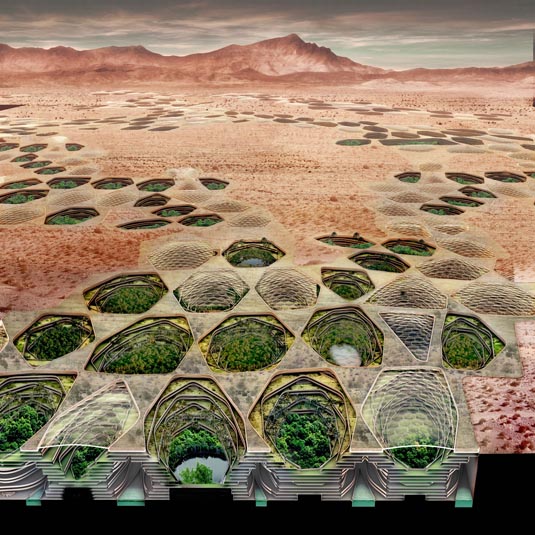 [Image: From
[Image: From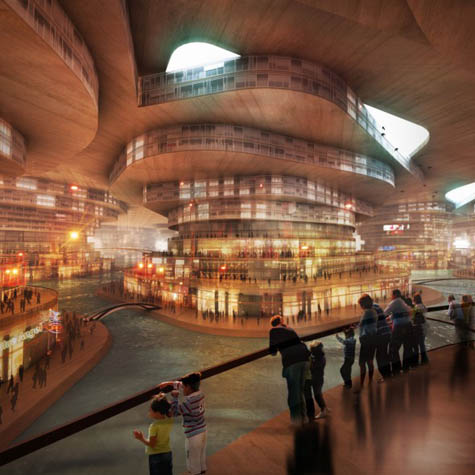  [Image: From
[Image: From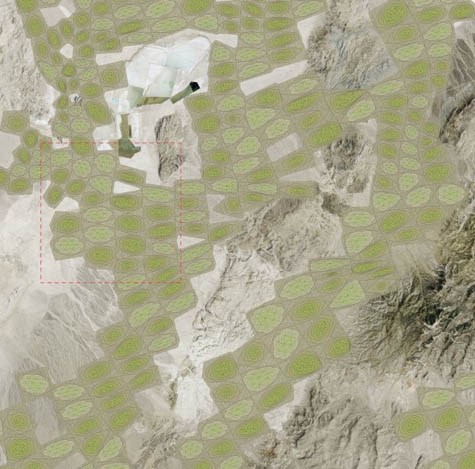  [Image: Matsys’s
[Image: Matsys’s  [Image: “
[Image: “ [Image: “
[Image: “ [Images: Screen grabs from James Cameron’s Aliens].
[Images: Screen grabs from James Cameron’s Aliens].
 [Images: “
[Images: “ [Image: “
[Image: “
 [Images: “
[Images: “ [Image: The Maunsell Sea Forts, photographed by Pete Speller, courtesy of
[Image: The Maunsell Sea Forts, photographed by Pete Speller, courtesy of  [Images: Photos by
[Images: Photos by 
 [Images: Photos by
[Images: Photos by  [Image: The Maunsell Sea Forts, photographed by Pete Speller, courtesy of
[Image: The Maunsell Sea Forts, photographed by Pete Speller, courtesy of 

 [Images: Inside the forts; photos by Pete Speller, courtesy of
[Images: Inside the forts; photos by Pete Speller, courtesy of 




 [Images: Photos by Pete Speller, courtesy of
[Images: Photos by Pete Speller, courtesy of  [Image: From
[Image: From  [Image: A project by
[Image: A project by  [Image: A project by
[Image: A project by  [Image: A project by
[Image: A project by  [Image: The diagram of architectural outlines that was laser-cut into the book’s pages, recreating the illusory volume of a cinematic space].
[Image: The diagram of architectural outlines that was laser-cut into the book’s pages, recreating the illusory volume of a cinematic space]. [Image: A project by
[Image: A project by 
 [Images: Another project by
[Images: Another project by 
 [Images: By
[Images: By  [Image: Courtesy of the
[Image: Courtesy of the  [Image: Courtesy of the
[Image: Courtesy of the 
 [Image: Courtesy of the
[Image: Courtesy of the  [Image: Courtesy of the
[Image: Courtesy of the  [Image: Courtesy of the
[Image: Courtesy of the  [Image: Courtesy of the
[Image: Courtesy of the  [Image: Courtesy of the
[Image: Courtesy of the  [Image: From
[Image: From  [Image: From Jared Tarbell’s
[Image: From Jared Tarbell’s 
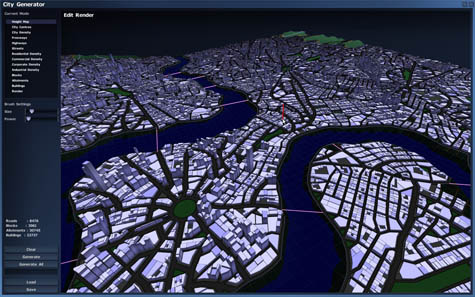 [Images: From Chris Delay’s
[Images: From Chris Delay’s  [Image: From
[Image: From  [Image: From Chris Delay’s
[Image: From Chris Delay’s  [Image: By
[Image: By  [Image: From Marco Corbetta’s Structure].
[Image: From Marco Corbetta’s Structure].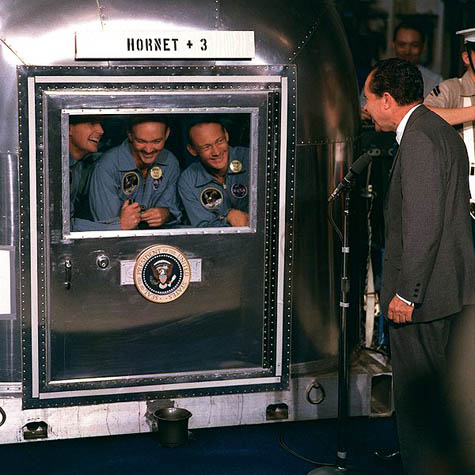 [Image: President Nixon addresses
[Image: President Nixon addresses  [Image: “Fear of Flu” by
[Image: “Fear of Flu” by 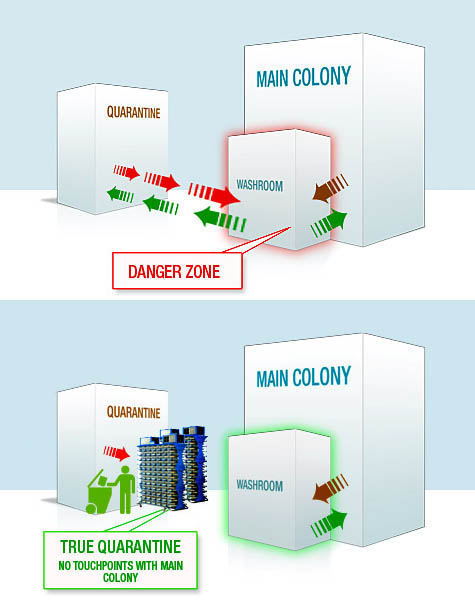 [Image: Cages for the laboratory testing of rats and mice by
[Image: Cages for the laboratory testing of rats and mice by  [Image: A poster for
[Image: A poster for  [Image: Australian
[Image: Australian