In the forests of northern Ontario, a “strange phenomenon” of large natural rings occurs, where thousands of circles, as large as two kilometers in diameter, appear in the remote landscape.
 [Image: From the thesis “Geochemistry of Forest Rings in Northern Ontario: Identification of Ring Edge Processes in Peat and Soil” (PDF) by Kerstin M. Brauneder, University of Ottawa].
[Image: From the thesis “Geochemistry of Forest Rings in Northern Ontario: Identification of Ring Edge Processes in Peat and Soil” (PDF) by Kerstin M. Brauneder, University of Ottawa].
“From the air, these mysterious light-coloured rings of stunted tree growth are clearly visible,” the CBC explained back in 2008, “but on the ground, you could walk right through them without noticing them.”
Since they were discovered on aerial photos about 50 years ago, the rings have baffled biologists, geologists and foresters… Astronomers suggest the rings might be the result of meteor strikes. Prospectors wonder whether the formations signal diamond-bearing kimberlites, a type of igneous rock.
While it’s easy to get carried away with visions of supernatural tree rings growing of their own accord in the boreal forest, this is actually an example of where the likely scientific explanation is significantly more interesting than something explicitly otherworldly.
 [Image: From the thesis “Geochemistry of Forest Rings in Northern Ontario: Identification of Ring Edge Processes in Peat and Soil” (PDF) by Kerstin M. Brander, University of Ottawa].
[Image: From the thesis “Geochemistry of Forest Rings in Northern Ontario: Identification of Ring Edge Processes in Peat and Soil” (PDF) by Kerstin M. Brander, University of Ottawa].
As geochemist Stew Hamilton suggested in 1998, the rings are most likely to be surface features caused by “reduced chimneys,” or “big centres of negative charge that frequently occur over metal deposits,” where a forest ring is simply “a special case of a reduced chimney.”
Reduced chimneys, meanwhile, are “giant electrochemical cells” in the ground that, as seen through the example of forest rings, can affect the way vegetation grows there.
 [Image: Screen-grab from Google Maps].
[Image: Screen-grab from Google Maps].
One of many things worth highlighting here is this suggestion that the trees are being influenced from below by ambient electrochemical processes in the soil, set into motion by the region’s deep geology:
Hamilton was testing an analytical technique over a Matheson gold deposit to determine if there was any kind of geochemical surface signal. To his surprise, there were signals coming through 30 to 40 metres of glacial clay.
“We’re thinking there’s no way metals can move through clay 10,000 years after glaciation.”
After ruling out transport by ground water, diffusion and gas, he theorized it had to have been lifted to surface on electrical fields.
He applied the same theory to forest rings and discovered that they were also giant negatively charged cells.
Any source of negative charge will create a forest ring.
In landscape architecture terms, a forest ring—which Hamilton describes [PDF] as “a plant assemblage that is different from the surrounding forest making the features visible from the air”—could be seen as a kind of indirect electrochemical garden taking on a recognizably geometrical form without human intervention.
In effect, their shape is expressed from below. For ambitious future landscape designers, note that this implies a potential use of plantlife as a means for revealing naturally occurring electrical networks in the ground, where soil batteries and other forms of terrestrial electronics could articulate themselves through botanical side-effects.
That is, plant a forest; come back after twenty years; discover vast rings of negative electrochemical charge like smoke rings pushing upward from inside the earth.
Or, of course, you could reverse this: design for future landscape-architectural effects by formatting the deep soil of a given site, thus catalyzing subterranean electrochemical activity that, years if not generations later, would begin to have aesthetic effects.
 [Image: From the paper “Spontaneous potential and redox responses over a forest ring” (PDF) by Stewart M. Hamilton and Keiko H. Hattori].
[Image: From the paper “Spontaneous potential and redox responses over a forest ring” (PDF) by Stewart M. Hamilton and Keiko H. Hattori].
But it gets weirder: as Hamilton’s fieldwork also revealed, there is a measurable “bulge in the water table that occurs over the entire length of the forest ring with a profound dip on the ring’s outer edge.” For Hamilton, this effect was “beyond science fiction,” he remarked to the trade journal Northern Ontario Business, “it’s unbelievable.”
What this means, he explained, is that “the water is being held up against gravity” by naturally occurring electrical fields.
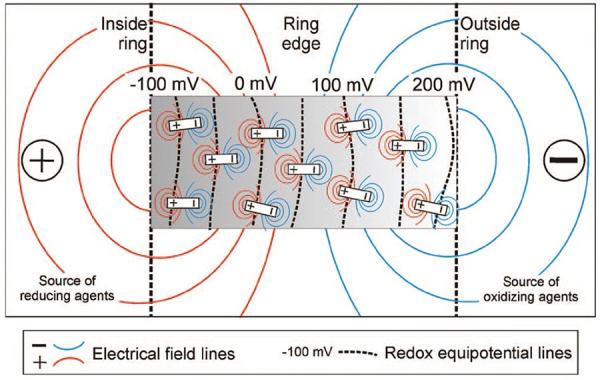 [Image: From the paper “Spontaneous potential and redox responses over a forest ring” (PDF) by Stewart M. Hamilton and Keiko H. Hattori].
[Image: From the paper “Spontaneous potential and redox responses over a forest ring” (PDF) by Stewart M. Hamilton and Keiko H. Hattori].
Subsequent and still-ongoing research by other geologists and geochemists has shown that forest rings are also marked by the elevated presence of methane (which explains the “stunted tree growth”), caused by natural gas leaking up from geological structures beneath the forest.
Hamilton himself wrote, in a short report for the Ontario Geological Survey [PDF], that forest ring formation “may be due to upward methane seepage along geological structures from deeper sources,” and that this “may indicate deeper sources of natural gas in the James Bay Lowlands.”
Other hypotheses suggest that these forest rings could instead be surface indicators of diamond pipes and coal deposits—meaning that, given access to an aerial view, you can, in effect, “read” the earth’s biosphere as a living tissue of signs or symptoms through which deeper, non-biological phenomena (coal, diamonds, metals) are revealed.
 [Image: Forest ring at N 49° 16′ 05″, W 83° 45′ 01″, via Google Maps].
[Image: Forest ring at N 49° 16′ 05″, W 83° 45′ 01″, via Google Maps].
Even better, these electrochemical effects stop on a macro-scale where the subsurface geology changes; as Hamilton points out [PDF], the “eastward disappearance of rings in Quebec occurs at the north-south Haricanna Moraine, which coincides with a sudden drop in the carbonate content of soils.”
If you recall that there were once naturally-occurring nuclear reactors burning away in the rocks below Gabon, then the implication here would be that large-scale geological formations, given the right slurry of carbonates, metals, and clays, can also form naturally-occurring super-batteries during particular phases of their existence.
To put this another way, through an accident of geology, what we refer to as “ground” in northern Ontario could actually be thought of a vast circuitboard of electrochemically active geological deposits, where an ambient negative charge in the soil has given rise to geometric shapes in the forest.
 [Image: Forest rings at N 49° 29′ 48″, W 80° 05′ 40″, via Google Maps].
[Image: Forest rings at N 49° 29′ 48″, W 80° 05′ 40″, via Google Maps].
In any case, there is something incredible about the idea that you could be hiking through the forests of northern Ontario without ever knowing you’re surrounded by huge, invisible, negatively charged megastructures exhibiting geometric effects on the plantlife all around you.
Several years ago, I wrote a post about the future of the “sacred grove” for the Canadian Centre for Architecture, based on a paper called “The sacred groves of ancient Greece” by art historian Patrick Bowe. I mention this because it’s interesting to consider the forest rings of northern Ontario in the larger interpretive context of Bowe’s paper, not because there is any historical or empirical connection between the two, of course; but, rather, for the speculative value of questioning whether these types of anomalous forest-effects could, under certain cultural circumstances, carry symbolic weight. If they could, that is, become “sacred groves.”
Indeed, it is both thrilling and strange to imagine some future cult of electrical activity whose spaces of worship and gathering are remote boreal rings, circular phenomena in the far north where water moves against gravity and chemical reactions crackle outward through the soil, forcing forests to take symmetrical forms only visible from high above.
For more on forest rings, check out the CBC or Northern Ontario Business or check out any of the PDFs linked in this post.


 [Image: Tar pushes up through cracks in the sidewalk on Wilshire Boulevard, near the La Brea Tar Pits; photo by Geoff Manaugh].
[Image: Tar pushes up through cracks in the sidewalk on Wilshire Boulevard, near the La Brea Tar Pits; photo by Geoff Manaugh]. [Image: A makeshift system for capturing the near-constant tar and liquid asphalt leaking up from below a building near Lafayette Park; photo by
[Image: A makeshift system for capturing the near-constant tar and liquid asphalt leaking up from below a building near Lafayette Park; photo by  [Image: Liquid asphalt leaking upward into the parking lot of a Los Angeles karaoke club; photo by Geoff Manaugh].
[Image: Liquid asphalt leaking upward into the parking lot of a Los Angeles karaoke club; photo by Geoff Manaugh].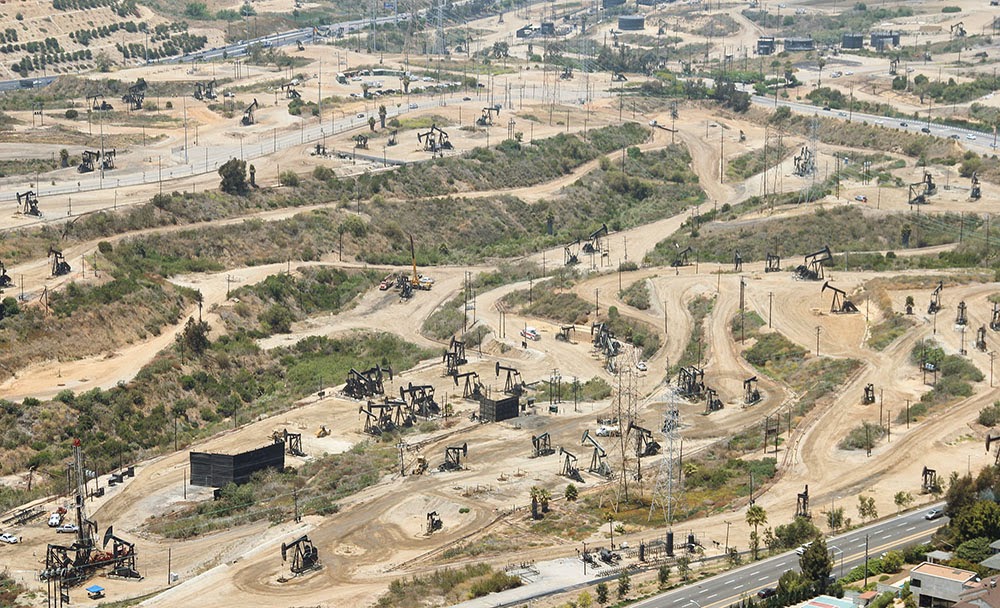 [Image: The Baldwin Hills old field; photo by Geoff Manaugh].
[Image: The Baldwin Hills old field; photo by Geoff Manaugh]. [Image: Screen grab from
[Image: Screen grab from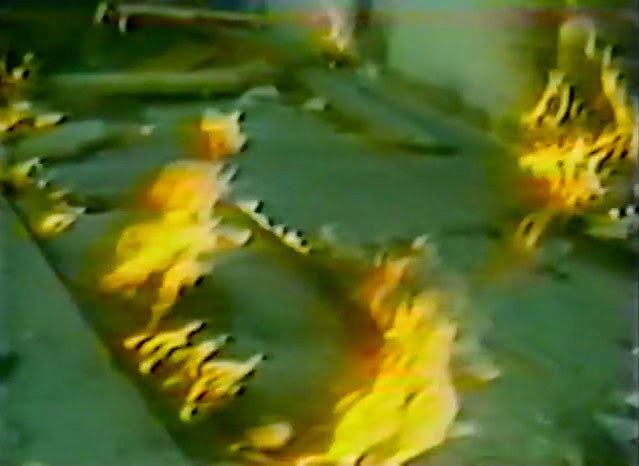  [Image: Flames burn through cracks in the sidewalk; screen grab from
[Image: Flames burn through cracks in the sidewalk; screen grab from