One of many books I’ve been enjoying this autumn is On Monsters by Stephen T. Asma, an extended look into where formal deviation occurs in the world and what unexpected, often emotionally disconcerting, shapes and forces can result.
 [Image: The Dariel Pass in the Caucausus Mountains, rumored possible site of the mythic Alexander’s Gates].
[Image: The Dariel Pass in the Caucausus Mountains, rumored possible site of the mythic Alexander’s Gates].
According to Asma, measuring these swerves and abnormalities against each other—and against ourselves—can shed much-needed light on the alternative “developmental trajectories” by which monsters come into being. This speculative monsterology, as he describes it it, would thus uncover the rules by which even the most stunning mutational transformations occur—allowing us to catalog extraordinary beings according to what Asma calls a “continuum of strangeness: first, nonnative species, then familiar beasts with unfamiliar sizes or modified body parts, then hybrids of surprising combination, and finally, at the furthest margins, shape-shifters and indescribable creatures.” Asma specifically mentions “mosaic beings,” beings “grafted together or hybridized by nature or artifice.”
In the book’s fascinating first-third—easily the book’s best section—Asma spends a great deal of time describing ancient myths of variation by which monsters were believed to have originated. From the mind-blowing and completely inexplicable discovery of dinosaur bones by ancient societies with no conception of geological time to the hordes of “monstrous races” believed to exist on the imperial perimeter, there have always been monsters somewhere in the world’s geography.
Of specific relevance to an architecture blog, however, are Alexander’s Gates.
 [Image: Constructing the wall of Dhul-Qarnayn, mythic isotope to Alexander’s Gates].
[Image: Constructing the wall of Dhul-Qarnayn, mythic isotope to Alexander’s Gates].
Alexander’s Gates, Asma writes, were the ultimate wall between the literally Caucasian West and its monstrous opponents, dating back to Alexander the Great:
Alexander supposedly chased his foreign enemies through a mountain pass in the Caucasus region and then enclosed them behind unbreachable iron gates. The details and the symbolic significance of the story changed slightly in every medieval retelling, and it was retold often, especially in the age of exploration.
(…) The maps of the time, the mappaemundi, almost always include the gates, though their placement is not consistent. Most maps and narratives of the later medieval period agree that this prison territory, created proximately by Alexander but ultimately by God, houses the savage tribes of Gog and Magog, who are referred to with great ambiguity throughout the Bible, and sometimes as individual monsters, sometimes as nations, sometimes as places.
Beyond this wall was a “monster zone.”
 [Image: The geography of Us vs. Them, in a “12th century map by the Muslim scholar Al-Idrisi. ‘Yajooj’ and ‘Majooj’ (Gog and Magog) appear in Arabic script on the bottom-left edge of the Eurasian landmass, enclosed within dark mountains, at a location corresponding roughly to Mongolia.” Via Wikipedia].
[Image: The geography of Us vs. Them, in a “12th century map by the Muslim scholar Al-Idrisi. ‘Yajooj’ and ‘Majooj’ (Gog and Magog) appear in Arabic script on the bottom-left edge of the Eurasian landmass, enclosed within dark mountains, at a location corresponding roughly to Mongolia.” Via Wikipedia].
Interestingly, a variation of this story is also told within Islam—indeed, in the Koran itself. In Islamic mythology, however, Alexander the Great is replaced by a figure called Dhul-Qarnayn (who might also be a legendary variation on the Persian king Cyrus).
Even more interesting than that, however, the Koran’s own story of geographically distant monsters entombed behind a vast wall—the border fence as theological infrastructure—appears to be a kind of literary remix of the so-called Alexander Romance. To quote that widely known religious authority Wikipedia, “The story of Dhul-Qarnayn in the Qur’an… matches the Gog and Magog episode in the Romance, which has caused some controversy among Islamic scholars.” That is, the Koran actually includes a secular myth from 3rd-century Greece.
The construction of Dhul-Qarnayn’s wall against the non-Muslim monstrous hordes can specifically be found in verses 18:89-98. For instance:
“…Lend me a force of men, and I will raise a rampart between you and them. Come, bring me blocks or iron.”
He dammed up the valley between the Two Mountains, and said: “Ply your bellows.” And when the iron blocks were red with heat, he said: “Bring me molten brass to pour on them.”
Gog and Magog could not scale it, nor could they dig their way through it.
Think of it as a kind of religious quarantine—a biosafe wall through which no moral contagion could pass.
 [Image: Constructing the wall of Dhul-Qarnayn, via Wikipedia].
[Image: Constructing the wall of Dhul-Qarnayn, via Wikipedia].
But as with all border walls, and all imperial limits, there will someday be a breach.
For instance, Asma goes on to cite a book, published in the 14th century, called the Travels of Sir John Mandeville. There, we read how Alexander’s Gates will, on some future day blackened by the full horror of monstrous return, be rendered completely obsolete:
In the end, Mandeville predicts, a lowly fox will bring the chaos of invading monsters upon the heads of the Christians. He claims, without revealing how he comes by such specific prophecy, that during the time of the Antichrist a fox will dig a hole through Alexander’s gates and emerge inside the monster zone. The monsters will be amazed to see the fox, as such creatures do not live there locally, and they will follow it until it reveals its narrow passageway between the gates. The cursed sons of Cain will finally burst forth from the gates, and the realm of the reprobate will be emptied into the apocalyptic world.
In any case, the idea that the line between human and not-human has been represented in myth and religion as a very specifically architectural form—that is, a literal wall built high in the mountains, far away—is absolutely fascinating to me.
Further, it’s not hard to wonder how Alexander’s Gates compare, on the level of imperial psychology, to things like the Great Wall of China, the Berlin Wall, the U.S./Mexico border fence, or the Distant Early Warning Line—even London’s Ring of Steel—let alone the Black Gates of Mordor in Tolkien’s Lord of the Rings.
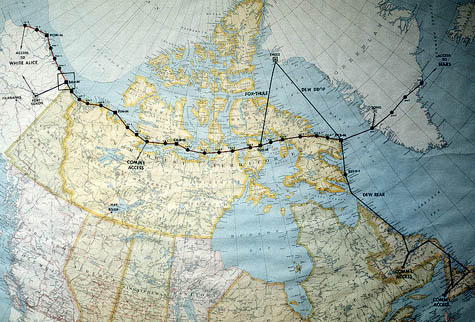 [Image: A map of the Distant Early Warning Line, an electromagnetic Alexander’s Gates for the Cold War].
[Image: A map of the Distant Early Warning Line, an electromagnetic Alexander’s Gates for the Cold War].
Perhaps there is a kind of theological Hyperborder waiting to be written about the Wall of Gog and Magog.
Or could someone produce an architectural history of border stations as described in world mythology? I sense an amazing Ph.D. research topic here.
 [Image: Spiral Arches by Daydreamers Design].
[Image: Spiral Arches by Daydreamers Design]. [Image: Spiral Arches by Daydreamers Design].
[Image: Spiral Arches by Daydreamers Design].
 [Images: Spiral Arches by Daydreamers Design].
[Images: Spiral Arches by Daydreamers Design].

 [Images: Spiral Arches by Daydreamers Design].
[Images: Spiral Arches by Daydreamers Design]. [Image: The Dariel Pass in the Caucausus Mountains, rumored possible site of the mythic
[Image: The Dariel Pass in the Caucausus Mountains, rumored possible site of the mythic  [Image: Constructing the wall of Dhul-Qarnayn, mythic isotope to Alexander’s Gates].
[Image: Constructing the wall of Dhul-Qarnayn, mythic isotope to Alexander’s Gates]. [Image: The geography of Us vs. Them, in a “12th century map by the Muslim scholar Al-Idrisi. ‘Yajooj’ and ‘Majooj’ (Gog and Magog) appear in Arabic script on the bottom-left edge of the Eurasian landmass, enclosed within dark mountains, at a location corresponding roughly to Mongolia.” Via
[Image: The geography of Us vs. Them, in a “12th century map by the Muslim scholar Al-Idrisi. ‘Yajooj’ and ‘Majooj’ (Gog and Magog) appear in Arabic script on the bottom-left edge of the Eurasian landmass, enclosed within dark mountains, at a location corresponding roughly to Mongolia.” Via  [Image: Constructing the wall of Dhul-Qarnayn, via
[Image: Constructing the wall of Dhul-Qarnayn, via  [Image: A map of the
[Image: A map of the  [Image:
[Image: