Several months ago we looked at a network of artificial caves being built beneath Singapore that will, upon completion, extend the city’s energy infrastructure under the Pacific seabed; and, back in 2010, we took a very brief look at huge excavations underneath Chicago, courtesy of a feature article in Tunnel Business Magazine.
Now, according to the South China Morning Post, civil engineers in Hong Kong are exploring the possibility of developing large-scale underground spaces—artificial caves—for incorporation into the city’s existing infrastructure. In the full text of the article, available online courtesy of Karst Worlds, we read that the Hong Kong government “is moving towards burying bits of the city—the unsightly ones—in underground caverns, freeing up more land for housing and economic development.”

 [Image: From the Enhanced Use of Underground Space in Hong Kong].
[Image: From the Enhanced Use of Underground Space in Hong Kong].
This is part of a larger undertaking called the Enhanced Use of Underground Space in Hong Kong initiative, a study, backed by Arup, that “would give the government a basis for policy guidelines to encourage cavern developments for both public and private sectors.” Private-sector caverns beneath the city!
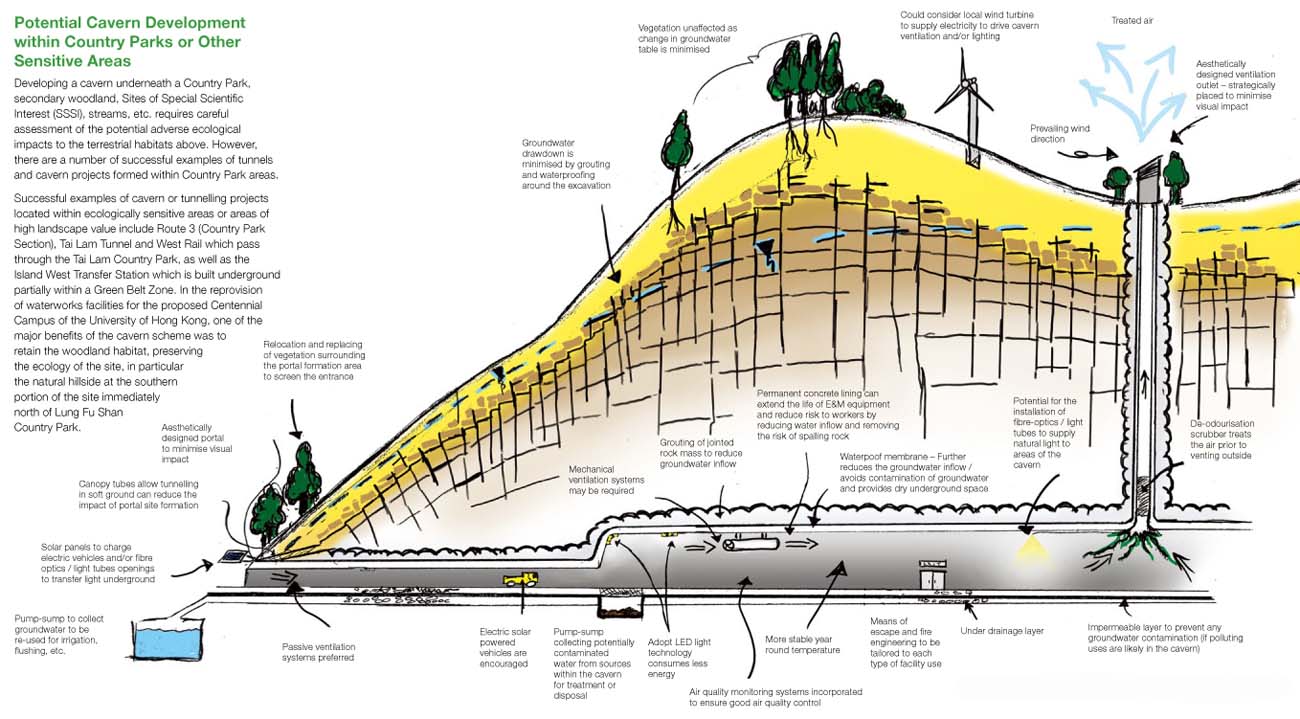 [Image: From the Enhanced Use of Underground Space in Hong Kong; view bigger].
[Image: From the Enhanced Use of Underground Space in Hong Kong; view bigger].
Specifically, city engineers “will begin by identifying suitable rock caverns to house 400 government facilities that can be relocated, notably the not-in-my-backyard utilities disliked by nearby residents.” These include “sewage treatment plants, fuel storage depots, refuse transfer stations and columbariums.” The University of Hong Kong, for instance, recently “hid a saltwater reservoir in an artificial cavern next to its Centenary Campus, in a project that cost HK$500 million”; these are referred to as “water caverns.”
Inspired by the fact that “caverns have been used as wine cellars, data centres and car parks in Finland and other countries,” Hong Kong’s Secretary of Development, Carrie Lam, has “called Hong Kong’s rock formations a ‘unique geological asset‘ and urged the city to take caverns into consideration.”
 [Image: From the Guide to Cavern Engineering].
[Image: From the Guide to Cavern Engineering].
The awesome scale of some of the proposed excavations can be seen in this animation, where, at roughly the one-minute mark, we dive underground and begin to fly through linked 3D models of future freshwater reservoirs. A related PDF outlines a new landscape category—the Strategic Cavern Area—wherein “a strategic area is defined as being greater than 20 hectares in area and having the ability to accommodate multiple cavern sites.” (The idea that your neighborhood might be declared a Strategic Cavern Area, and thus cleared of its building stock, brings to mind a student project featured on BLDGBLOG last month, the “Lower East Side Quarry” by Rebecca Fode).
 [Images: From the Guide to Cavern Engineering].
[Images: From the Guide to Cavern Engineering].
Sadly, we missed an opportunity to participate in a Hong Kong-based cave-design contest—its deadline was September 2011—called the “Rock Caverns—Unlimited Creativity” competition: “Competition entrants are required, with their unlimited creativity, to propose ideas related to the potential usage of underground space in Hong Kong.” A detailed design guide, called the Geoguide or Guide to Cavern Engineering, was published, and it remains available in full online.
This booklet is nothing less than a builder’s guide to artificial caves. As Chapter 4 helpfully explains, for instance, “In common with other complex constructions, the design of a large underground space is an iterative process where a series of factors influence the final result,” with prospective cave-designers required to use “numerous iterative loops” to create “a cost-effective cavern installation.” The rest of that chapter goes on to explore cavern cross-sections, layout, shape, rock bolts and pattern bolting, and even intra-cave pillars, all of which should find their way into an architecture school design studio somewhere soon.
 [Image: From the Guide to Cavern Engineering].
[Image: From the Guide to Cavern Engineering].
In any case, while I feel compelled to point out the obvious—that a high-tech labyrinth of artificial caves dug beneath the rocky hills of an over-urbanized tropical archipelago is an incredible setting for future films, novels, and computer games—I should also mention, more prosaically, that Hong Kong’s impending subterranean expansion will doubtless offer many lessons relevant to cities elsewhere, as public-private underground partnerships increase in both number and frequency, with space-starved global mega-cities turning to partial self-burial as a volumetric infrastructural solution to the lack of available surface area.
