Bracket 2 has been announced. This second issue of the annual design almanac seeks “critical articles and unpublished design projects that investigate physical and virtual soft systems, as they pertain to infrastructure, ecologies, landscapes, environments, and networks.”
 [Image: Fabric urbanism: a “tent city,” via Bracket].
[Image: Fabric urbanism: a “tent city,” via Bracket].
If soft systems are, as the editors maintain, “a counterpoint to permanent, static and hard systems,” then what benefits do they bring, under what circumstances do they function best, and, of course, what do they look like (if they can be seen at all)?
While there is more information on Bracket‘s site, including some historical background on the emergence of soft systems in architectural planning and design, via figures such as Nicholas Negroponte and even Archigram, this issue of the journal is specifically looking for the following:
Bracket 2 seeks to critically position and define soft systems, in order to expand the scope and potential for new spatial networks, and new formats of architecture, urbanization and nature. From soft politics, soft power and soft spaces to fluid territories, software and soft programming, Bracket 2 questions the use and role of responsive, indeterminate, flexible, and immaterial systems in design. Bracket 2 invites designers, architects, theorists, ecologists, scientists, and landscape architects to position and leverage the role of soft systems and recuperate the development of the soft project.
For my own part, I’m increasingly interested in the design and implementation of what might be called soft medical infrastructure—or temporary, sometimes even inflatable, field hospitals and other on-demand medical facilities.
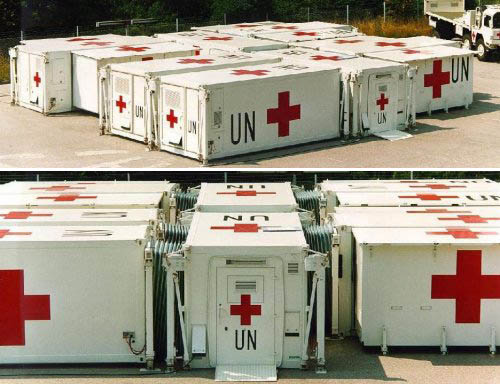 [Image: A “containerized” field hospital by the Red Cross and UN].
[Image: A “containerized” field hospital by the Red Cross and UN].
From a “modular air-transportable field camp” that has been “tested at the Arctic Circle” to first-responder architecture deployed on the scene of natural disasters, fires, acts of war, and terrorist attacks—and even by way of the somewhat ominous-sounding “systems for peacekeepers” devised by Kärcher Futuretech, down to the level of mobile catering units for use in remote landscapes and even inside warzones—how are architectural and infrastructural networks pushed into new design directions by extreme events?
 [Image: Deployable Incident Command Post (ICP) by Reeves].
[Image: Deployable Incident Command Post (ICP) by Reeves].
Submissions are due before December 10, 2010, with a Fall 2011 publication date; the resulting book will be designed by Thumb and published by Actar.
Consider picking up a copy of Bracket 1: On Farming, meanwhile, to see how the journal works and what sorts of projects they might be looking for.
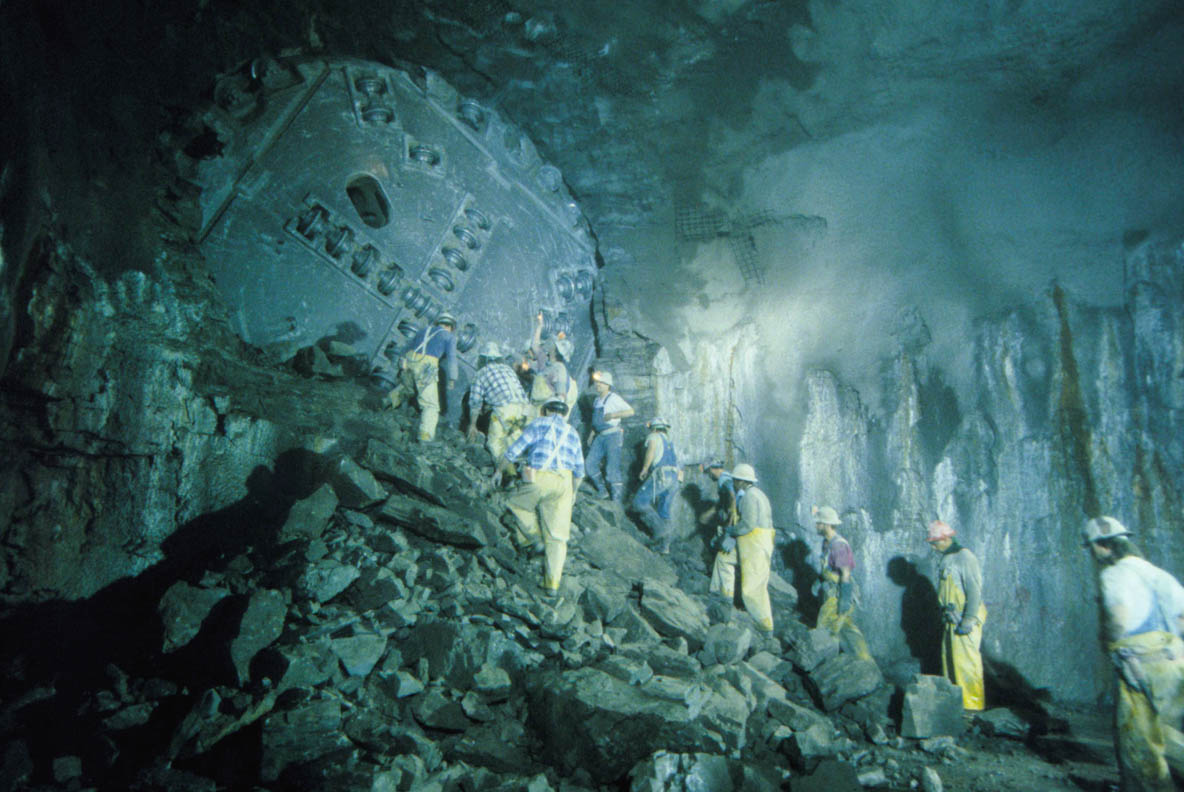
 [Image: Tunneling beneath Chicago;
[Image: Tunneling beneath Chicago; 
 [Image: From Robocop, via
[Image: From Robocop, via  [Image:
[Image:  [Image: A “
[Image: A “ [Image:
[Image:  [Image: An outdoor
[Image: An outdoor  [Image: The
[Image: The 
 [Image: The German cover of
[Image: The German cover of 
 [Image: A future site for Austin + Mergold’s
[Image: A future site for Austin + Mergold’s 
 [Images:
[Images: 
 [Images:
[Images: 
 [Image: Jack Whitten prepping octopi on the rocky coast; photo via
[Image: Jack Whitten prepping octopi on the rocky coast; photo via  [Image: Jack Whitten prepping octopi on the rocky coast; photo via
[Image: Jack Whitten prepping octopi on the rocky coast; photo via  [Image: “Seeing-Outlook” (2001) from
[Image: “Seeing-Outlook” (2001) from  [Image: From
[Image: From  [Image: “Snowballs” (2001) from
[Image: “Snowballs” (2001) from  [Image: “Sphere at Dawn” (2003) from
[Image: “Sphere at Dawn” (2003) from  [Image: “Winternight” (2001) from
[Image: “Winternight” (2001) from 
 [Images: “Antenna Forest” (2000) and “Sunken Ship” (2001), from
[Images: “Antenna Forest” (2000) and “Sunken Ship” (2001), from 
 [Images:
[Images:  [Image:
[Image: 






 [Images:
[Images: 
 [Image: Sellafield; photo courtesy of
[Image: Sellafield; photo courtesy of 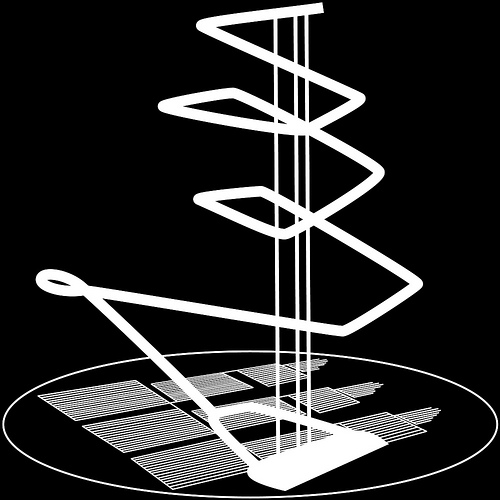 [Image: A circulation diagram of the underground nuclear waste repository at Onkalo, Finland, from
[Image: A circulation diagram of the underground nuclear waste repository at Onkalo, Finland, from  [Image: The entryway to Onkalo’s moribund underworld, from Michael Madsen’s
[Image: The entryway to Onkalo’s moribund underworld, from Michael Madsen’s