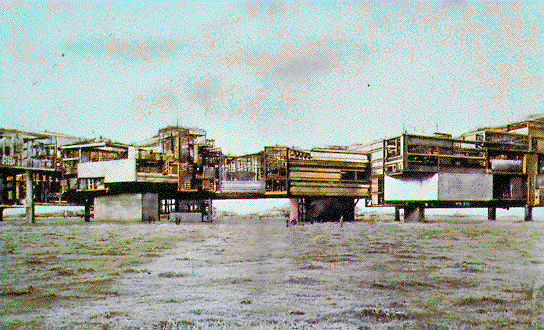
 [Image: The Bay Line by Ronald Rael and Virginia San Fratello; modular additions can be seen bolted on from below. Read the project PDF].
[Image: The Bay Line by Ronald Rael and Virginia San Fratello; modular additions can be seen bolted on from below. Read the project PDF].
Combining Rails to Trails, William Gibson’s Virtual Light, and the same repurposed-preservation strategies behind New York’s High Line, Bay Area architects Ronald Rael and Virginia San Fratello have called for stabilizing the disused – and soon to be entirely dismantled – portion of the Bay Bridge. They would then turn it into a pedestrianized urban park and outdoor sports attraction.
 [Image: The Bay Bridge and its replacement; on the right is the piece that Rael San Fratello would like to see stabilized. Image via Wikipedia].
[Image: The Bay Bridge and its replacement; on the right is the piece that Rael San Fratello would like to see stabilized. Image via Wikipedia].
And if it works for the Bay Bridge, they suggest, it could work for other disused bridges elsewhere.
“This proposal seeks to repurpose abandoned and closed bridges as sites of potential for parks, cultural centers and housing,” the architects write in the project’s accompanying PDF. In the process, they hope “to demonstrate the potential for re-purposing historic American bridge infrastructure as possible sites for sustainable urban housing and linear parks.”
The immense load capacity of rail bridges allows for the support of program beyond that of parks, suggesting the urbanization of bridges. While the current economic climate suggests a surplus of housing, the economic reality also suggests a push towards urbanization and often the “affordable” housing constructed in suburban environments, which encroaches on the rural, is not what is needed. Instead, by using abandoned bridges in urban areas, we are creating opportunities for sustainable low-cost housing within the urban realm—creating the potential for creative speculation among housing developers by expounding upon the nascent potential of a layered housing-park-bridge typology.
While, on one level, this simply side-steps the immense financial implications associated with structurally maintaining these bridges, and, on another level, it bears an unfortunate resemblance to Boris Johnson’s recent – if not necessarily well-received – call for an inhabitable bridge across the Thames, it does also kick-start a conversation about what we might be able to do with the massive pieces of civic infrastructure that dot the U.S. and are currently scheduled for replacement and demolition.
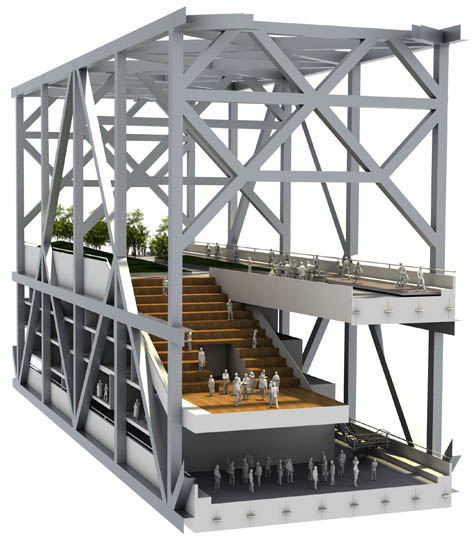


 [Images: (top) Tennis court, bicycle path, and observation module; (middle) Outdoor auditorium; (bottom) swimming pool on the Bay Line by Ronald Rael and Virginia San Fratello].
[Images: (top) Tennis court, bicycle path, and observation module; (middle) Outdoor auditorium; (bottom) swimming pool on the Bay Line by Ronald Rael and Virginia San Fratello].
And, I have to admit, it would simply be cool:
Imagine housing, recreational and cultural facilities connected to a continuous, lushly planted, green strip, floating above the water—an aerial garden, as the city’s newest park through which you could walk and wander and enjoy the most spectacular views of the bay.
Of course, critics like James Howard Kunstler might suggest that reusing rail infrastructure – or, in this case, highway infrastructure – as anything other than a rejuvenated national rail service is “decadence at its purest,” it is surely just as decadent to watch as functional pieces of infrastructure rot on all sides, as you sit there with your arms crossed, waiting for the nation’s taxpayers to agree with your views on reuse.
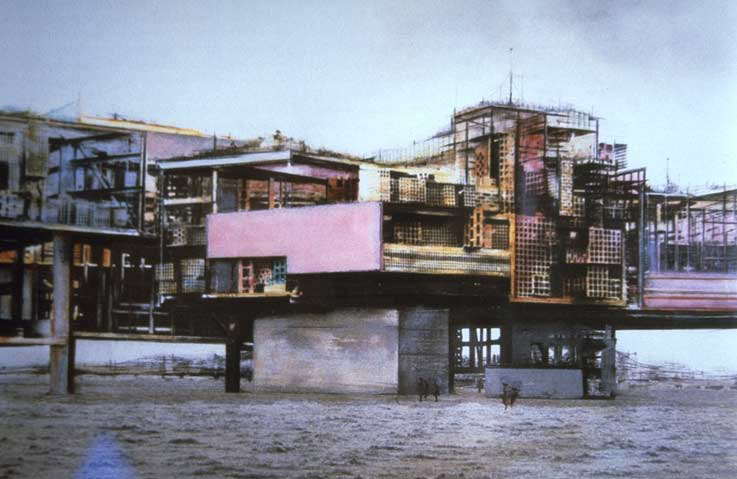

 [Images: Other habitable bridge: (top) Florence’s Ponte Vecchio; (second) a painting by Peter Jackson of “Old London Bridge“; (third and bottom) Constant’s New Babylon].
[Images: Other habitable bridge: (top) Florence’s Ponte Vecchio; (second) a painting by Peter Jackson of “Old London Bridge“; (third and bottom) Constant’s New Babylon].
In any case, as someone who literally never enjoyed driving across the Bay Bridge for seismic-safety reasons, I have to point out that this proposal still comes with its own set of earthquake-related issues. I was interested, however, to read in the Economist just this week that “there are few safe places to ride out an earthquake. Surprisingly, though, a recently constructed bridge is often one of them.”
Engineers have become good at designing bridges that are earthquake-resistant enough to preserve the lives of those caught crossing when a quake strikes. The problem is that the bridge is often unusable afterwards.
Nonetheless, if you had put millions of dollars’ worth of landscape and housing onto a bridge that was then left abandoned and “unusable” after an earthquake, it would be a very foolhardy investment, indeed.
 [Image: Final render of the Bay Line by Ronald Rael and Virginia San Fratello].
[Image: Final render of the Bay Line by Ronald Rael and Virginia San Fratello].
But what of bridges in non-seismic zones? In Sydney, for instance, due to the peninsular nature of walks along Cremorne Point and through Kirribilli, there are places where the Sydney Harbor Bridge appears not to be crossing over water at all, but standing over the rooftops of the city, anchored into the neighborhood. It looks more like a new kind of inland megastructure, strung above the streets and restaurants, like something designed by Perdido Street Station-era China Miéville, than a harbor bridge. An industrial cathedral of exposed ribs and steel tension lines, arcing up into the skyline.
So what if you hung houses from it? What amazing typologies of bolt-on architectural prosthetics could we create, if bridges were aerial foundations and they carried not cars or locomotives but schools and piazzas?
In fact, I’m reminded of this unexpectedly inspiring – structurally speaking – proposal by Skidmore, Owings & Merrill, which sought to string the suspension cables of a new pedestrian bridge from inside the nearby buildings of a rebuilt Leamouth Peninsula (click through to their image gallery for more).
 [Image: A proposal for London’s Leamouth Peninsula by Skidmore, Owings & Merrill].
[Image: A proposal for London’s Leamouth Peninsula by Skidmore, Owings & Merrill].
Returning to Rael San Fratello‘s Bay Line, though, there are obviously still huge issues associated with the unusually catastrophic nature of structural failure when it comes to inhabitable bridges, as well as the financially prohibitive needs of regular maintenance, but treating suspension bridges simply as another type of district in the city is an undeniably interesting urban idea.
(Via Streetsblog SF and Ronald Rael. Meanwhile, Rael’s recently published book Earth Architecture is an excellent and thoughtful survey of earthen structures across the world and throughout building history; Rael’s old school blog, megablog, is also worth a read for its eye-popping and often literally world-altering architectural ambitions).
Interesting article – I have always wanted to see that bridge from 'Die Hard' built … one of the reasons i got into deigning the built environment i think! As a side note – the SOM bridge at Leamouth is actually designed by Thomas Heatherwick, a true design genius and very much a modern day Da Vinci I reckon…
re: bridges that don't appear to cross water: Bern, Switzerland, has an interesting bridge that for most of its length is over an inhabited part of the city.
Here's the bridge:
http://www.pbase.com/edhahn/image/68466879
And here's a pic taken from the bridge:
http://www.pbase.com/edhahn/image/68145102
Regarding the Bay Bridge project: a Berkeley student did a very similar proposal for his architecture thesis a few years ago, but without having the bulk of the housing suspended below the deck. The thing is, if it is suspended, it reduces the clearance down below for boats in the shipping channel…
Very interesting. the bottom pictures have caught my attention more than the others right off the bat. Just the pure structural mass in its self makes it a very interesting proposal. It causes a lot of high tension from the bands coming out of the other buildings and acting as a support for the bridge its self.
This is super cool. I wrote my undergraduate thesis last spring about elevated urban public space, both in utopian conception and built realization… it seems like even since May, when I handed the thesis in, there's been so much more attention given to these kinds of urban space than ever before.
The opening of the High Line has a lot to do with it, but I think it also has to do with the economic downturn… when the money dries up, and there's more impetus to think about public projects, people suddenly have the time and energy to think outside the box… on paper. But (High Line excepted, because it was high-profile enough and politically acceptable enough to be profitable for the city, and had been planned and committed to before the recession really began) it'll be another question whether any of these ideas actually get built.
Question for people: are spaces like this a fad that's inseparably bound to the recent trends making cities hipper, fancier, and less economically diverse? Or is there potential for these spaces to emerge as a new and healthy kind of urban form (like the park, or the plaza, or the bridge), independent of age-specific trends that may happen to be associated with them right now? (As an analogue, the "skyway" that connects the downtowns of cities like Minneapolis and Calgary has been often critcized as an unhealthy urban form, even by those cities where the systems still exist. The form never really escaped the problems of the particular, fraught context in which it sprang up.)
(If anyone's interested, you can get to the paper I wrote here. Beware the large file size… it's long and highly illustrated!)
I am doing my undergraduate thesis on Habitable bridges.
I couldn’t find the report in the link u mentioned.
It would be a great help if can u send me the report.
vysakh.v.p@gmail.com
It would appear this would require a commitment to a substantial investment. The question is how much would it cost to build, how much to maintain, how many people would it house and how much would be the rent. Once the numbers are put together by those familiar with building offshore oil platforms, the decision makers can make plans to do it or not.
Firstly it reminded me of the rather bad Johnny Mnemonic with Keanu Reeves . It was a suspended urban slum and also anti-corporate rebel hideout . Although there's new abilities to accommodate the 2 different typologies , it'll probably be as usual a good long while until sufficient urban pressure to see it widespread .
reminds me of my favorite park in paris, france: the promenade plantée (or, coulée verte) which used to be a railway viaduct connecting the bastille to the suburbs in the east.
…really? How about just doing something worthwhile and cover the entire surface with solar arrays? you could power a good portion of the city, or at least the governmental buildings. The city could recoup the cost of the arrays and installation in probably no more than a year.
Great to see Constant's New Babylon again after 50 years.
What about wind? The Mackinaw Bridge sways as much as 30 feet back and forth in high winds. Wouldn't this make residents (not bicyclists or pedestrians) sick? It's still a cool concept if all of the engineering can be resolved. Where would you park? What about fire department access and hydrants?
This really seems incredibly impractical.
Limited or no access for vehicles -what about emergencies?
this is of course insane
the bridge is unsound
engineering studies estimate it would cost billions to seismically retrofit and that was just to be used as the existing roadway without addition