 [Image: A thoughtfully signposted British flood; photo by Matt Cardy for Getty Images].
[Image: A thoughtfully signposted British flood; photo by Matt Cardy for Getty Images].
I’m totally fascinated by the idea that adventure tourism firms might someday lead wreck-diving tours through the flooded ruins of London: in your expensive re-breathing gear, you’ll roll backward off a boat, flashlight in hand… and the coral-specked vaults of St. Paul’s are now yours to explore.
All the churches of Nicholas Hawksmoor, as seen through a diving mask. Or the Tube, full of moray eels, awaiting the truly brave.
Fantastically, that’s not so unrealistic an image – because London, after all, is sinking.
Using satellite measurement, tide gauges, GPS, and a few other devices called “absolute gravimeters,” a new study proves that London is moving downward into the Earth’s surface in “a general pattern of subsidence of 1-2mm a year. With waters rising in the region by about 1mm a year, the combined effect is a 2-3mm a year rise in sea level with respect to the land.”
The investigation confirms geologic studies that show the Earth’s crust is still responding to the loss of the heavy ice sheet which covered much of Britain more than 10,000 years ago – with southeast England, including London, slowly sinking.
Do some basic math, and that puts London under three meters of water in roughly 1000 years – and London, incredibly, will have passed through the other side of the planet in less than – whoa –
To help protect against these encoaching waters, the city contains or is surrounded by a rarely noticed hydrological labyrinth: “300km of tidal defences including embankments, walls, gates and barriers.”
However, “at some stage, [these will] have to be adapted or moved” – at least until “new types of defences [are] created that make better use of the natural floodplain.”
I love this stuff. In fact, I’m 100% convinced that if architectural magazines really wanted to discuss what the London of tomorrow will look like, they’d have stopped talking to architects a long time ago – and they’d have flood consultants on the phone.
The future of London will be determined by hydrological engineers.
 [Image: The Tewkesbury flood of 2007, as seen from the air; photo by Daniel Berehulak for Getty Images].
[Image: The Tewkesbury flood of 2007, as seen from the air; photo by Daniel Berehulak for Getty Images].
In any case, London is also jostling up and down on the Earth’s surface, everyday, bobbing up and down like a buoy with the tides; these micro-movements need to be taken into account by anyone who hopes to study the effects of so-called post-glacial rebound.
London itself will rock by 10mm, twice a day, with loading from ocean tides. The seasons also alternately load and unload the ground, making the Earth’s crust “breathe” up and down over a longer period.
London, your tides are breathing you. An Albionic lung.
But if you want more stuff like that, this older post is rather heavy on British hydro-speculation.
Meanwhile, a “lost” village in Wiltshire might offer a glimpse of London’s own future to come. From the BBC:
A team of divers who set out to solve the mystery of the drowned village of Bowood in Wiltshire has found the remains of buildings under a lake.
If that sounded easy, though, consider that “[p]revious attempts to find the village included a dive by Bowood owner Lord Lansdowne, the 9th Marquis of Lansdowne, who donned his scuba gear 20 years ago. His attempt was unsuccessful.”
So will aquatic archaeologists someday dive into the kelp-choked canyons of what was once Islington High Street, looking for lost malls and cinemas…?
This blogger thinks so.
Moving on: in an amazing story that was reported – and repeated – all over the place last week, we learned that a thin ridge of chalk once connected SE England to NW France.
The image, below, is BLDGBLOG’s own highly inaccurate, and grossly out of scale, representation of what that ridge might have looked like.
 Calculated to stop the hearts of English people the world over, those maps show us a land-bridge, continentalizing Kent, putting Franco in the Anglo and de-Saxonizing the island from its royal isolation. And I have no idea what that sentence means, either.
Calculated to stop the hearts of English people the world over, those maps show us a land-bridge, continentalizing Kent, putting Franco in the Anglo and de-Saxonizing the island from its royal isolation. And I have no idea what that sentence means, either.
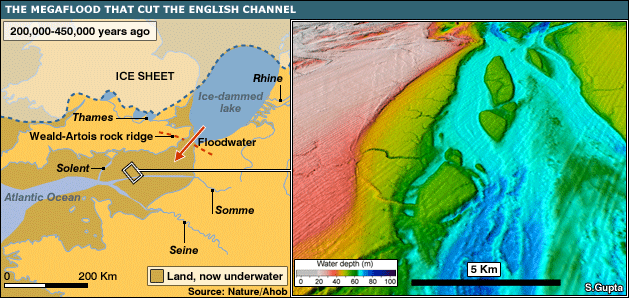 [Image: A slightly more accurate map of both the chalk ridge and the glacial lake it held back; via the BBC].
[Image: A slightly more accurate map of both the chalk ridge and the glacial lake it held back; via the BBC].
According to New Scientist: “Half a million years ago, Britain was connected to mainland Europe by a broad chalk ridge that spanned what we now call the Dover Strait. But somehow that ridge was destroyed, forever separating England and France.”
A new theory holds that this ancient chalk ridge was “breached and toppled by a monumental torrent that gushed from an overfilling glacial lake that the ridge had been damming on its northern side.” As evidence of its passing, the catastrophic flood left “deep valleys gouged into the channel’s bedrock,” turning what is now England, Scotland, and Wales into one big happy island.
“At its peak,” the BBC adds, “it is believed that the megaflood could have lasted several months, discharging an estimated one million cubic metres of water per second.”
However, New Scientist quietly points out that Alec Smith, of Bedford College, London, once suggested this exact same idea, back in 1985 – and he was ridiculed. Nobody believed him.
Sorry, Alec.
Finally, it would have been hard to miss all the news about last week’s floods across England – so I’ll just supply these links and let the pictures do the talking.
 [Image: The Tewkesbury flood of 2007, as seen from the air; photo by Daniel Berehulak for Getty Images].
[Image: The Tewkesbury flood of 2007, as seen from the air; photo by Daniel Berehulak for Getty Images].
But, of course, England has a deep history of flooding…
(Note: The Wiltshire lost village link was discovered via an amazing post at things magazine, a reliable source of great links and information – for anyone out there who doesn’t already know it).
You’ll probably never have to dive to see Islington high street – it’s on top of a hill. North London shouldn’t be affected much for a very long time.
The paleo-hydrologists in this article may be worth tracking down. They have computer models of the North Sea Basin when the overlying water was locked up in glaciers. Sorry only the abstract appears to be available on line: http://www.archaeology.org/0701/abstracts/northsea.html
Turns out drowned cultural landscapes can be bigger than the odd flooded village (common under reservoirs around the world) or sunken cathedral. Consider thousands of square miles of once-dry continental shelf (and the drowned forests, and forest settlements, investigators are finding doing EIS’s for off-shore wind farms).
Beats Kevin Costner in Waterworld hands down…
I wouldn’t mind this place being attached to France.
Instead of building the Chunnel they ought to have filled the channel in, Dutch style, and dug a tunnel for shipping running it’s entire length.
Funnily enough, I’m serious(ish), except for the shipping tunnel, naturally. They can go ’round.
Ah, I can see it now:
The old man sat in a second row chair in the Lady Chapel, resting his head, meditatively, on the Red Book he held against the top of the seat in front of him. Seemingly alone in the vast spaces of the Anglican cathedral — the sacred place his fellow Liverpudlians called “Dracula’s castle” — he imagined the weight of the twelve massive bells so high above him, silent now. He was afraid to stand directly beneath them, though he could not see them. But in the Lady Chapel he felt safe.
A strange noise made him raise his head. Above him, in a serene and celestial blue light that seemed to flow and flicker across the walls, a figure moved. A diver descended. The ghost vanished.
It is horrible.
btw: a new blog about contemporary architecture in china. maybe interesting.
oops. forgot the address:
http://archichina.blogspot.com/
This scenario is something being explored in a new film called ‘flood’ … stills showing what might happen to London can be found on the Sky News website – http://news.sky.com/skynews/picture_gallery/0,,70141-1277500,00.html
reminds me of that Radiohead video for “Pyramid Song”.
http://video.google.com/videoplay?docid=8138281894352463527
Some people get on the verge of bonkers ideas … if you fill in the East of England with the Thames Barrage sediment, Thamesgate, the Olympic leap and the Chunnel with rocks the flow from Rhine will have to go all the way around Scotland, SE England and northern France will sink faster, although I think it is recovering as Scotland settles back quietly post Ice. There are many other Tectonic features as Alpine forces push north and African plates select new locations, Australia moves farther east north and many people find many more sub-plates. The Atlantic trench is thickening, the Pacific more thin and tilt and plate interactions Nazca Pacific against these explain much of subduction Andean and volcano Indian Ocean Pacific ring, shock p-compression earthquakes, frequent lately. It also upsets ship owners who like to run bulk at cheap cost with few landings especially on Scots beaches during Atlantic storms. The only severe need for SE England London is civil engineering drainage and they said that in NCE publicly in 1982, as our streets compact under heavy traffic load slowly into the alluvium. Make yourselves responsible for it in perpetuity by all means, but you will be digging it and washing it down for decades if you do and it must not affect other people's drainage.