 [Image: Map Measuring Tool, CIA].
[Image: Map Measuring Tool, CIA].
The U.S. Central Intelligence Agency has uploaded a massive set of images from their historic mapping unit to Flickr.
 [Image: Triangular 24-Inch Engineering Scale, CIA].
[Image: Triangular 24-Inch Engineering Scale, CIA].
The collections include state-of-the-art graphic tools for producing maps and other measured cartographic products, as well as the maps themselves. Organized by the decade of its production—including batches from the 1940s, 1950s, and 1960s—“each map is a time capsule of that era’s international issues,” as Allison Meier points out.
 [Image: Terrain map of the Sinai Peninsula (1950s), CIA, CIA].
[Image: Terrain map of the Sinai Peninsula (1950s), CIA, CIA].
“The 1940s include a 1942 map of German dialects,” Meier writes, “and a 1944 map of concentration camps in the country. The 1950s, with innovative photomechanical reproduction and precast lead letters, saw maps on the Korean War and railroad construction in Communist China. The 1960s are punctuated by the Cuban Missile Crisis and Vietnam War, while the 1970s, with increasing map automation, contain charts of the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan, and the Arab oil embargo.”


 [Images: The Austin Photo Interpretometer, CIA].
[Images: The Austin Photo Interpretometer, CIA].
But it’s the mapping tools themselves that really interest me here.
On one level, these graphic devices are utterly mundane—triangular rulers, ten-point dividers, and interchangeable pen nibs, for example, any of which, on its own, would convey about as much magic as a ballpoint pen.
 [Image: 10-Point Divider, CIA].
[Image: 10-Point Divider, CIA].
Nonetheless, there is something hugely compelling for me in glimpsing the actual devices through which a country’s global geopolitical influence was simultaneously mapped and strategized.

 [Images: Rolling Disc Planimeter, CIA].
[Images: Rolling Disc Planimeter, CIA].
As the CIA points out, their earliest mapping division “produced some 8,000 hand-drawn maps and 64 plaster topographic 3-D models in support of the war effort. Many of their products played crucial roles in the planning and execution of major military operations in the European, North African, and Asian Theaters. On display here are just some of the many tools that OSS cartographers employed in their production process.”
 [Image: Dietzgen Champion Drawing Instruments, CIA].
[Image: Dietzgen Champion Drawing Instruments, CIA].
In a sense, it’s not unlike seeing the actual typewriter with which a particular author wrote her novels, or the battered, handheld sketchbooks a painter once carried with him to a distant mountaintop—only here, in art historical terms, we are looking at the graphic tools and visual documents through which a country’s overseas influence was realized and maintained.
It is a narrative of covert state power as relayed through cartographic objects, the outlines of an imperial nation-state arising from them like a ghost.
 [Image: Stanley Improved Pantograph, CIA].
[Image: Stanley Improved Pantograph, CIA].
I’m reminded of one of my favorite books on the subject of geopolitics, literally understood: Rachel Hewitt’s Map of a Nation: A Biography of the Ordnance Survey.
Among other things, Hewitt’s book reveals the often deeply strange tools—including surreal glass rods—through which British mapmakers and other agents of terrestrial exploration measured their nascent empire, helping to transform landscape into a mathematized system of coordinates and, in the process, conveying to British authorities the exact volumetric extent of their political domain.
There was the empire, in other words—but there were also these exotic objects of measurement through which that same empire was conjured, as if through cartographic magic.
 [Image: Keufel & Esser 20.5-inch Slide Rule, CIA].
[Image: Keufel & Esser 20.5-inch Slide Rule, CIA].
In any case, check out more at the CIA’s “Cartography Tools” Flickr set.
(Originally spotted via Alessandro Musetta).

 [Image: Internal title page from
[Image: Internal title page from 
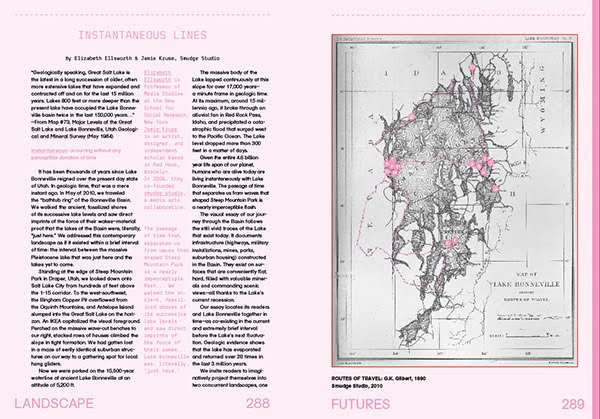

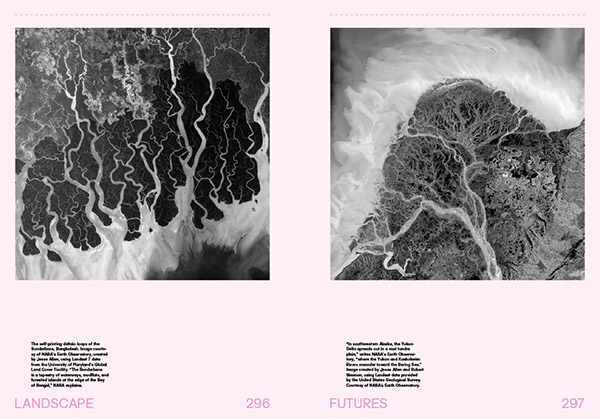 [Images: A few spreads from the “Landscape Futures Sourcebook” featured in
[Images: A few spreads from the “Landscape Futures Sourcebook” featured in 
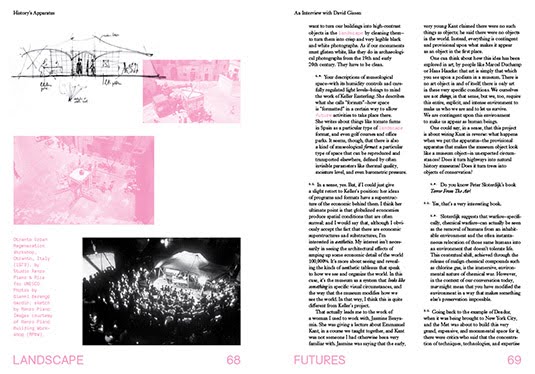

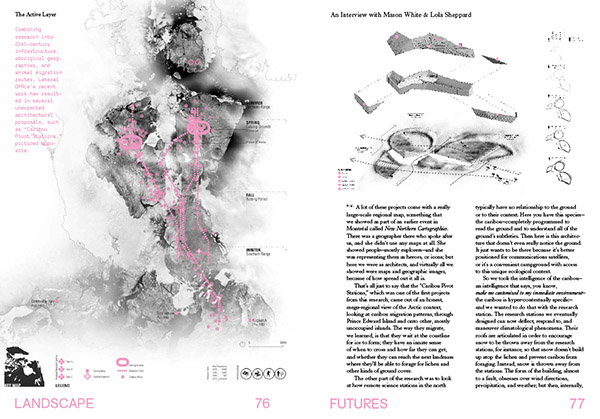








 [Images: Interview spreads from
[Images: Interview spreads from 
 [Image: From “
[Image: From “ [Image: From “
[Image: From “

 [Images: From “
[Images: From “ [Images: From “
[Images: From “ [Image: From “
[Image: From “